Man-in-the-middle attacks are just another thing we must worry about when using modern technology. Each threat comes with its own set of rules and dangers. However, MITM attacks present end users with a serious challenge. If you aren’t careful, you could end up losing everything.
Keep reading this guide to find out what a man-in-the-middle attack is, how it works, some examples, their purpose, and how to stay safe from MITM attacks.
The man-in-the-middle attack explained
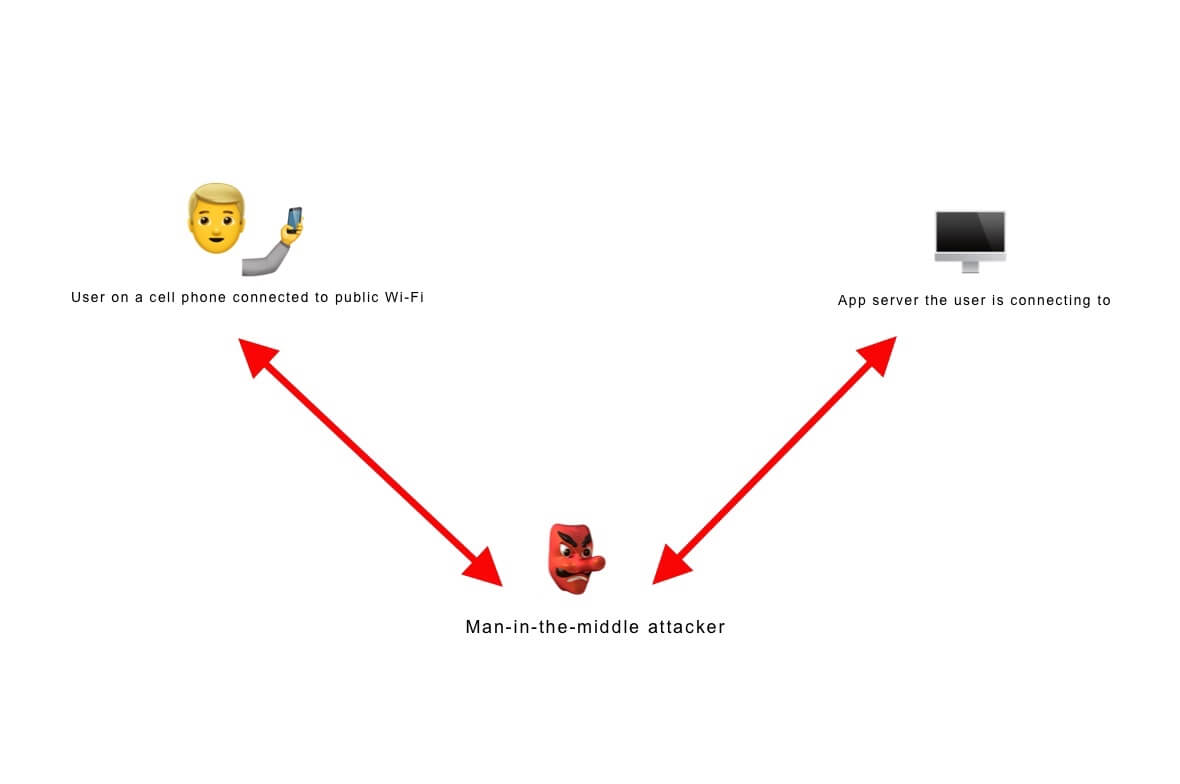
A man-in-the-middle attack is when a cybercriminal eavesdrops on a conversation between two people or devices on a network. The two targets don’t have to be users. They could be servers or apps communicating data back and forth. Typically, it involves a user communicating with an application or a website.
Some types of MITM attacks include:
- DNS spoofing
- IP spoofing
- Email hijacking
- Wi-Fi eavesdropping
- Https spoofing
- SSL hijacking
- Season hijacking
- ARP spoofing
- SSL stripping
- SSL BEAST
- Cache poisoning
In each case, cybercriminals use sniffing tools to identify vulnerable devices as targets. They often use penetration-testing resources like Ettercap, dSniff, and Cain and Abel. Although these tools were designed by engineers to identify network vulnerabilities, hackers have discovered their usefulness in selecting targets.
Man-in-the-middle attacks are extremely dangerous because they can result in the user losing control of their financial accounts. Many MITM perpetrators target bank and credit card account information.

Signs that your device might be an MITM attack victim are:
- A slow and unresponsive device: If your device disconnects from services that usually work fine, it could indicate an attack.
- An unrecognized Wi-Fi network: If your device connects to an unsecured network that you do not recognize, a hacker could be controlling it.
- Strange websites: When you visit the web, does the URL look strange (maybe one or two characters off from the regular site)? If so, you could be the victim of an MITM attack.
What is the purpose of an MITM attack?
The main goal of a man-in-the-middle attack is to steal private information like bank account numbers, login credentials, and credit card numbers. Financial gain is usually what the hacker is after.
Some bad actors use MITM attacks to grab personal information to use for identity theft or sell on the dark web.
Another reason bad guys use man-in-the-middle attacks is to gain access to a secure network by infecting a device (such as a user’s cell phone) as part of an advanced persistent threat (ATP) attack.
Examples of man-in-the-middle attacks
In 2014, computer giant Lenovo distributed new computers with Superfish Visual Search adware installed. Hackers used this vulnerable software to deploy fake ads on encrypted web pages and change the SSL to illegitimate versions. It allowed them to view web activity and copy login credentials while someone was using Chrome or Internet Explorer.
Similarly, in 2017, the Equifax credit bureau suffered a significant data breach, exposing the data of more than 143 million Americans. Equifax created a website (equifaxsecurity2017.com) to inform customers of whether they were included in the breach. Unfortunately, the website used a shared SSL, and bad actors altered DNS records on the server, redirecting users to a fake website where they then stole personal data.
How MTIM attacks work
Man-in-the-middle attacks rely on a two-step process to be successful. They are the interception and decryption stages.
Stage 1: Interception
Stage 1, interception, begins as the threat actor inserts themselves between the user and the application or server. They do this by infiltrating an insecure Wi-Fi network, creating their own unsecured Wi-Fi network, manipulating IP addresses, or creating a fake website and altering DNS records to direct the user there.
Stage 2: Decryption
The second stage, decryption, takes place after the hacker has caught the user in the trap. They then use sophisticated software to siphon off data, credentials, account information, etc. During this phase, they decrypt the data to be readable and usable. Sometimes, they access accounts and change user logins to lock out the actual account owner.
How to prevent a man-in-the-middle attack
Protecting all your devices is the first step in keeping your financial accounts and personal information safe. The following are some tips to prevent an MITM attack.
1. Avoid using public Wi-Fi
Do not connect to public Wi-Fi at the local coffee shop, hotel, or airport. These unsecured public networks are a virtual candy shop of opportunity for hackers.
2. Always use secure connections
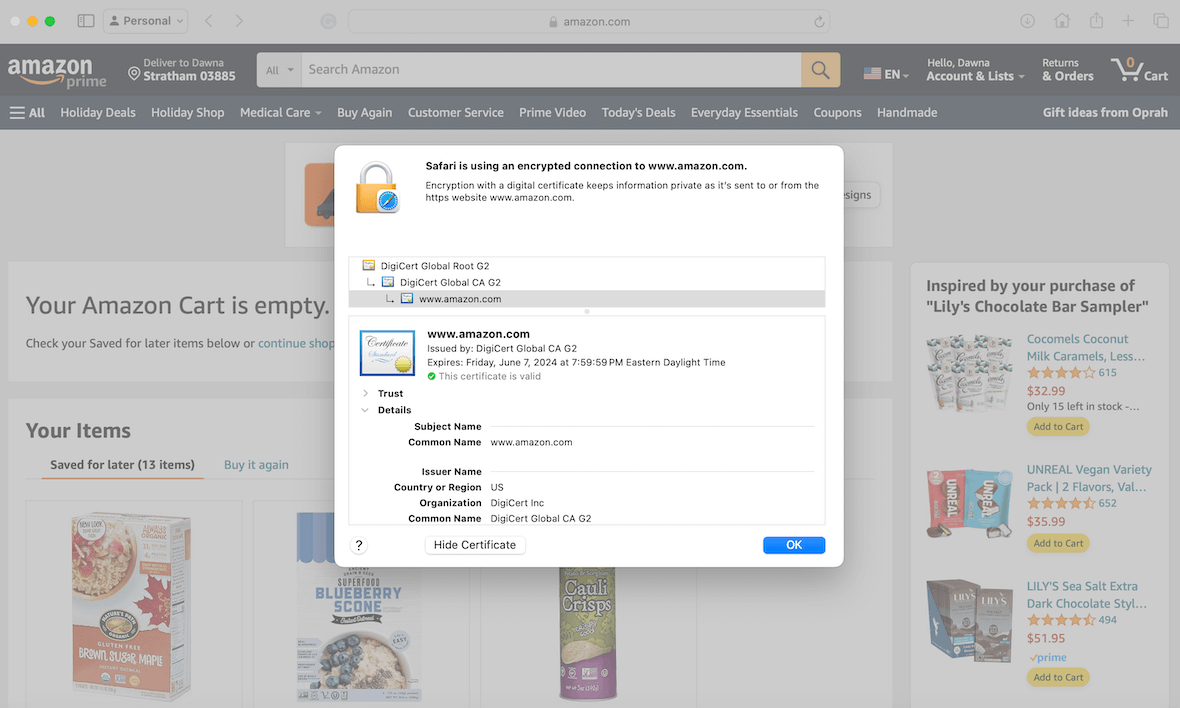
Only log on to websites that show the https protocol. Check the SSL (security certificate) to ensure that it is current and legitimate. However, keep in mind that SSLs can be hijacked, too. You can check this by clicking the lock in the address bar of Safari. When you see the pop-up, click Show Certificate. You will then see the details.
3. Verify before entering credentials
Check the URL to make sure it isn’t spoofed with extra letters or numbers. Sometimes, criminals use a website with a similar URL but with slight differences. Before entering any login credentials, confirm that you are on the proper site.
4. Log out when not in use
Log out of any applications or websites when you aren’t using them. Bad actors can use open sessions to infiltrate your accounts. Log out of devices, turn on 2FA (two-factor authentication) on all accounts, and use multi-factor authentication on all devices, making it harder for someone to take over.
5. Be watchful for phishing email attacks
Always watch out for phishing emails. Never click links inside an email. Instead, visit the website yourself by typing in the URL manually.
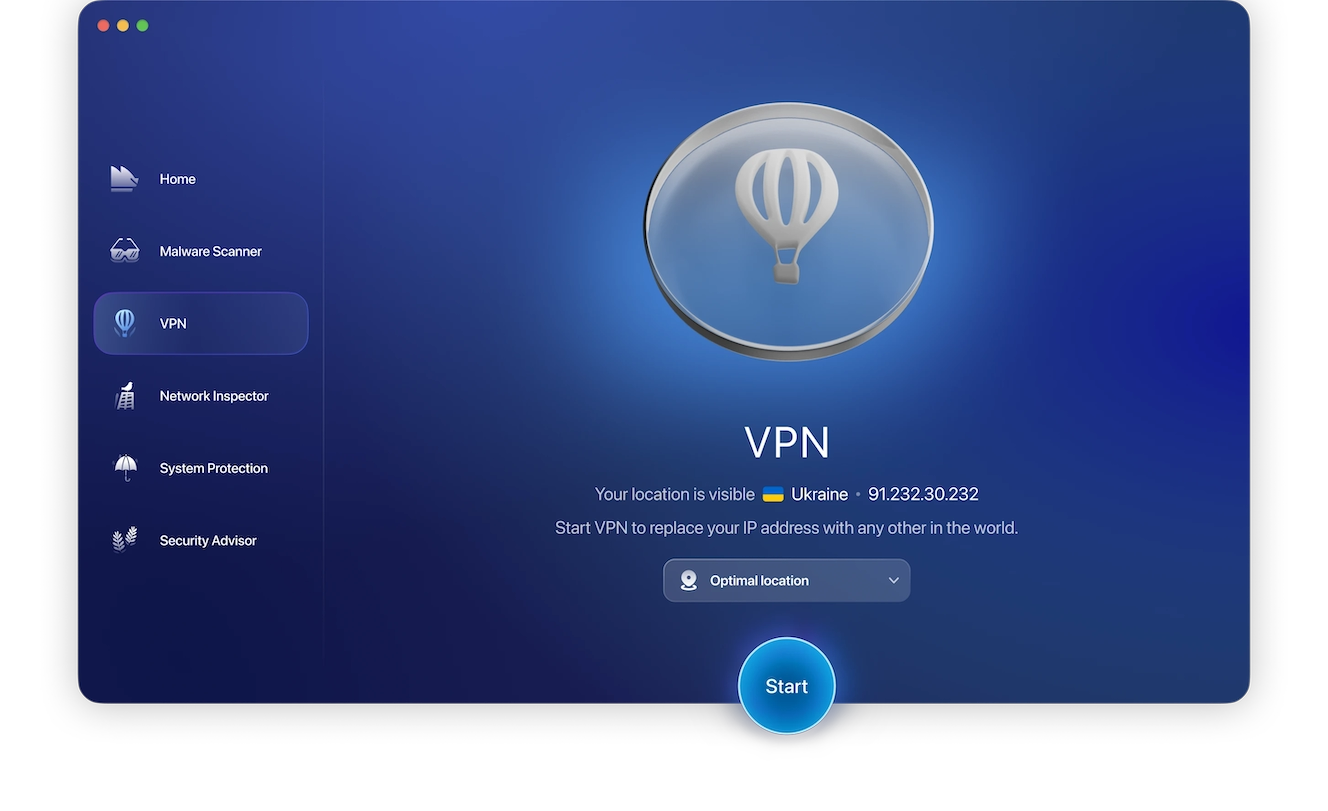
6. Use a VPN to mask your IP
Install a VPN to mask your IP address and hide all your online activities. A good VPN can keep you safe from man-in-the-middle attacks.
If you’re a Mac owner, you might benefit from the cybersecurity app Moonlock. It checks your network’s security settings and reminds you to turn on VPN when the connection might be risky.
- Sign up for your free trial and install Moonlock.
- Click System Protection in the sidebar and then hit Start. Moonlock will check system settings on your Mac, including your network.
- Once done checking, Moonlock will show you a list of recommendations to tighten macOS settings for better protection. If your network is unsafe, you’ll see a recommendation “Turn on VPN.”
- Press one button, and Moonlock will mask your IP with a random address anywhere in the world.
7. Use anti-malware software
Install anti-malware software on all your devices to keep intruders out and your device uninfected. Run routine scans to check for any abnormalities.
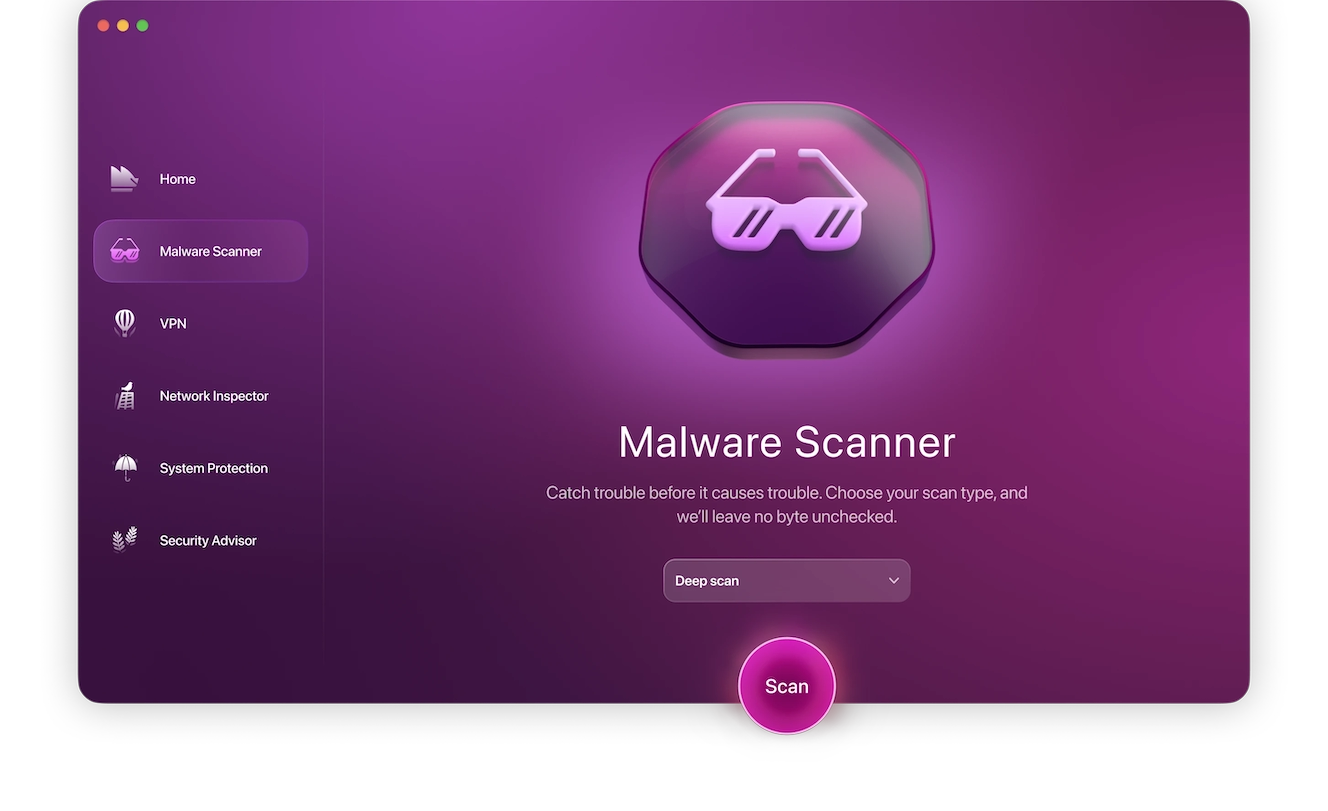
Install anti-malware software on all your devices to keep intruders out and your devices uninfected. Run routine scans to check for any abnormalities. Moonlock can help you out with that, too. Here’s how:
- Open Malware Scanner from the sidebar.
- In the drop-down menu, choose a type of scan you’d like to perform. The Quick option saves time but checks only the most vulnerable places on your Mac. A Deep scan takes more time and resources but leaves no byte unchecked.
- Click Scan. If any malware is found, it will be disarmed and locked away in Quarantine. From there, you can delete it anytime.
- If a file is mistakenly flagged and added to Quarantine, you can always unlock it and interact with it as usual.
As cybercriminals step up their game, you must do all you can to keep yourself safe. Educate yourself on the different types of attacks and use the tips in this guide to protect yourself from man-in-the-middle assaults.