A new threat is combining GitHub resources and Telegram bots to infect devices and install backdoor malware.
Researchers from Netskope recently found a new backdoor malware in the wild. While the malware is still under development and only targets Windows devices, it could easily be updated to target Apple devices and other operating systems.
Let’s look at this new threat, how it abuses and leverages Telegram, and how to stay safe.
Researchers go threat-hunting and find novel backdoor malware and techniques
Netskope Threat Labs researchers were performing their normal daily threat-hunting tasks when they came across an indicator of compromise (IoC) shared by the Malware Hunter Team on X (formerly Twitter).
After taking a deeper look into the threat, they discovered something rather unusual. The IoC belonged to malware that acted like a backdoor and used Telegram as its command and control (C2) channel.
Despite being under development, Netskope researchers found the malware to be fully functional.
Attribution and motive: Possible links to Russia and OT malware targeting critical infrastructure in Ukraine
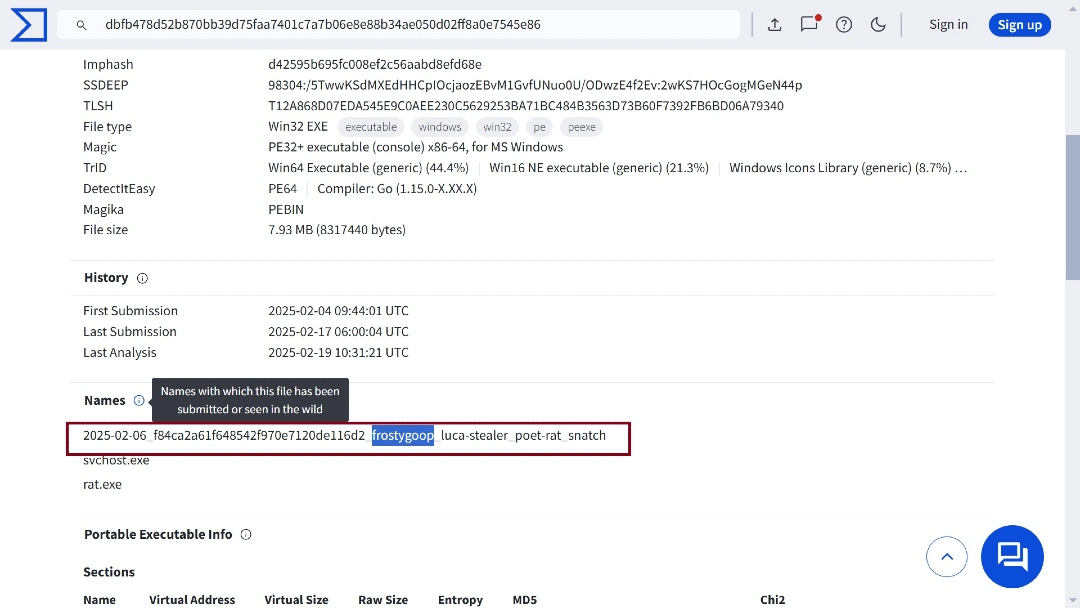
Moonlock looked at the files that spread this malware in the wild. Most of these files were named svchost.exe and rat.exe. However, another file that contained this malware was named 2024-12-12_3c886e525046ec4023362ab0a8a8a96e_frostygoop_luca-stealer_poet-rat_snatch.
Strangely enough, FrostyGoop is a loader malware linked to operational technology (OT) disruptions. Operational technology (OT) refers to the machines and technology equipment used in critical infrastructure industries such as health, energy, transportation, gas, or governments.
Palo Alto’s Unit 42 reported that the OT-centric malware FrostyGoop/BUSTLEBERM jumped into fame in mid-2024. It was used to disrupt critical infrastructure in Ukraine.
“The outage occurred after the Cyber Security Situation Center (CSSC), affiliated with the Security Service of Ukraine, disclosed details [PDF] of an attack on a municipal energy company in Ukraine in early 2024,” Palo Alto’s report reads.
While Netskope has not established who or what the developers of this new Go backdoor are targeting, the presence of the name of an OT malware in one of the files could imply that it was developed to attack the critical infrastructure sector.
This backdoor uses Telegram, a messaging app that is very popular in Russia and Ukraine and used by citizens, governments, and the military.
Analysis of the backdoor done by Netskope does not reveal the presence of any OT targeting code. Netskope said that the new backdoor malware is most likely of Russian origin.
Flexible and versatile malware and criminal infrastructure
The new backdoor, written in Go, uses a Telegram bot to exfiltrate information from infected devices and send commands to the malware. So far, the malware only has a couple of commands and can only target Windows devices. Still, the way the malicious infrastructure is set up speaks of danger and flexibility.
Backdoors are the most versatile malware in a hacker’s toolbox. They can be used to load any kind of malware onto an infected device, including ransomware, spyware, stealers, and more. Backdoors can also be accessed by attackers to modify systems, take over devices, and run commands.
This is how the backdoor uses Telegram bots to talk to infected devices
Cybercriminals use C2 servers to send commands to their malware and run processes on infected computers. The attacker-controlled C2 is where the exfiltrated, stolen data is sent, which is how bad actors control infected devices.
Operating a C2 with stealth and stability is challenging. Cybercriminals are constantly looking for new “places” to host their C2.
This new backdoor, which probably infects victims through phishing, malicious web pages, social media scams, or other methods, will first install itself and then create a communication channel using a new Telegram bot. The Telegram bot is how threat actors can send commands to the backdoor and receive data.
The developer or developers of this malware turned to GitHub resources and repositories to develop this threat. They also did their homework on how developers can create bots for Telegram.
As mentioned, while the malware only targets Windows devices for now, this method of using Telegram bots as C2s can be easily applied to macOS malware as well.
Netskope broke down this criminal trend and technique as follows:
“The backdoor uses Telegram as its C2 mechanism by using an open-source Go package to interact with it.”
“The first package function used is NewBotAPIWithClient, which is responsible for creating a bot instance based on a provided token created by the Telegram BotFather feature.”
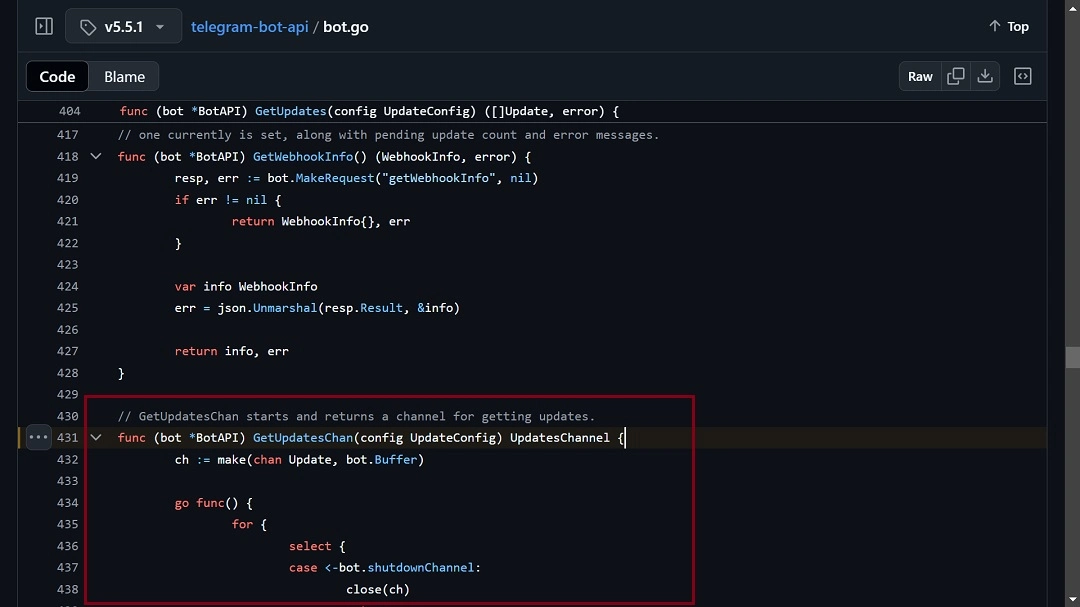
“It then calls the GetUpdatesChan (Go) function and creates a channel to keep checking if there’s new commands to be executed coming from the Telegram chat.”
So, there you have it. By using some simple GitHub resources, abusing Telegram bot capabilities, and turning to the simple but powerful Go programming language, cybercriminals can deploy backdoors that automatically create new bots in Telegram to use the popular but controversial service as a channel of communication for cybercrime.
7 ways to mitigate backdoors that use Telegram as a C2
Let’s look at 7 simple ways that this new type of threat can be mitigated by developers and users in general:
- Stay away from suspicious emails, contacts, links, and files: Malware infections have to start somewhere. Whether it is phishing emails, social media scams, or malicious websites, never click on unknown links, download suspicious attachments, or engage with unsolicited messages on platforms like Telegram.
- Limit the use of unauthorized software and repositories: Open-source is the foundation of all software, and every developer knows it. Therefore, we would not suggest that you stay away from free, efficient code. However, limit its use and only use repositories that are vetted.
- Monitor network traffic for unusual activity: If you have the knowledge and tools, an effective way to mitigate backdoors is by checking your traffic rates. Establish a baseline, and anything out of the ordinary should be a red flag. Backdoors are used to communicate with C2 attacker-controlled servers, so if there is one on your system, it will show up when monitoring outbound traffic, or it will flag unauthorized Telegram connections.
- Multi-layered security solutions: Enterprises should consider combining endpoint detection and response (EDR), threat intelligence, and behavior-based antivirus tools. These can help identify and mitigate threats before they execute.
- Make messaging as safe as possible: If you are using Telegram or other similar messaging apps, make sure you enable the strongest settings on your account’s security configurations. Use MFA and limit bot interactions. Be extra cautious about third-party bots. Also, enable encryption if it is not the default setting in your messaging app.
- Keep systems and software updated: Cybercriminals exploit unpatched vulnerabilities to gain access to devices. Therefore, regularly updating all software is good advice for developers and end users alike.
- Stay aware: Share cybersecurity news with your colleagues, leaders, and friends, and stay on top of breaking cybersecurity news to get the latest insights into new, evolving criminal techniques. This will help you stay one step ahead of scammers and online criminals.
By following this advice, you should increase your security posture significantly.
Final thoughts
While it is innovating to develop malware that can create Telegram bots and use a cloud messaging app as a C2 server, it is not surprising at all. We have seen cybercriminals host malware and abuse all types of devices and services, from edge to IoT to popular cloud sites.
In the era of automation, bots are also something to keep an eye out for. Cybercriminals use bots, including Telegram bots, 24/7, 365 days a year. Hopefully, this new backdoor technique will be mitigated before it is fully developed and operating in the wild.
This is an independent publication, and it has not been authorized, sponsored, or otherwise approved by Telegram Messenger Inc. Telegram is a trademark of Telegram Messenger Inc.