When most people hear the word “hacker,” they often think of the usual stereotype: an evil cybercriminal in a hoodie, hunched over a computer in a dark room. In a way, we have the media to thank for that depiction. However, this caricature is very unfair to a certain category of hacker whose intentions are not evil in the slightest. Quite the opposite, in fact.
What is white hat or ethical hacking?
There are several types of hackers, including the black hat hacker and the white hat hacker. The terms “black hat” and “white hat” indicate whether or not the hacker is using their hacking skills for good or bad. There are also hackers with other colors of “hats,” such as the red hat hacker, but that’s outside the scope of this article.
A black hat hacker is one who does hacking for illegal gain or to intentionally create havoc. This is the variety vilified in movies and TV shows as enemies of society. The ones who will empty out bank accounts and remotely hack into the electricity grid and shut it off.
On the flip side, a white hat hacker is more noble and principled (white being the color of purity and all). These hackers use their hacking skills to do good. They look for security vulnerabilities and report them to the affected entity. They also go after black hat hackers who are causing harm. Some even work for law enforcement.
Get a team of cyber pros to protect your Mac from malware
What does a white hat hacker do?
White hat hackers use the same skills cybercriminals use. But a white hat hacker will intentionally breach a system or scan through it with the aim of revealing bugs, misconfiguration, and vulnerabilities so they can be fixed. This often involves trying to get into the minds of cybercriminals, fighting fire with fire in the global cybersecurity crisis that affects all industries and sectors of the world.
Ethical hackers are gaining traction and solidifying their reputation for staying one step ahead of attackers. Today, white hat hackers are employed by organizations to put their systems to the test. Their job is to find the weak points before cybercriminals do. Organizations like HackerOne — the largest community of ethical hackers in the world, with more than one million registered hackers — offer their services to companies like Twitter, Facebook, Nintendo, GM, PayPal, and many others.

Is white hat hacking legal?
Because companies hire top ethical hackers to lead their security teams or as external contractors to test their systems, the work of white hat hackers is 100 percent legal. White hat hackers are respected and valued by the cybersecurity community.
New trends in white hat hacking include bounty programs. Several famous companies like Microsoft, Apple, Google, and others have offered thousands and even millions of dollars to white hat hackers who can hack newly released products and systems. Entire communities of white hat hackers search for vulnerabilities, malware, or other issues.
By contrast, black hat hackers are individuals who illegally hack systems or devices. Meanwhile, gray hat hackers are those who have good intentions but are willing to cross legal and ethical boundaries. Gray hat hackers operate without the permission of companies but do not have malicious intent. They are motivated by the challenge of hacking strong systems or exposing moral values.
How white hat hacking evolved
In the late 1950s, when there were no computers for personal use, a small group called the Phone Phreaks began hacking into the networks of public phone companies. They hacked into the phone network using a device known only as the Blue Box. This device imitated a specific set of audio tones. Although they could access a phone company’s system and make free calls, among other things, the motive for the hack was purely the thrill and the challenge.
This group inspired the first generation of hackers when Esquire ran a story about them titled “Secrets of the Little Blue Box” in October 1971, thus immortalizing the movement. The article made a big impression on Steve Wozniak, cofounder of Apple, and on Steve Jobs himself.
Silicon Valley computer clubs
By the 1970s, in the region known today as Silicon Valley, computer clubs began to form. These small groups of young people built their own computers and devices. Only governments and big industries used computers back then, but this movement of early white hat hackers led to the creation of companies like Apple and the evolution of IBM.

In the 80s and 90s, hacking entered a new phase. Personal computers were now a reality, and businesses had more at stake. This was the time when black hat and gray hat hackers began to flourish.
The rise of black hat hackers and regulations
While some hackers still only hacked for moral principles or technical challenges, by the late 1980s, the United States federal government stepped in to send a message to all hackers. Kevin Mitnick, known for hacking the computer giant Digital Equipment Corporation (DEC), was placed in the number-one spot on the FBI’s Most Wanted list. Today, Mitnick is one of the industry’s most-respected security consultants. However, his case and similar cases stigmatized hacking through new digital laws and robust prosecutions.
Today, the intense threat of a landscape driven by cybercriminal gangs, transnational criminal organizations, and global digitalization has reinvigorated the importance of the original hackers.
Notable examples of famous white hat hackers
Despite the stereotypical image of hackers lurking in dark rooms, there are some famous white hat hackers.
Kevin Mitnick

Kevin Mitnick might be the most well-known hacker of all time. Mitnick was once a black hat hacker who eventually ended up in prison in 1998 for 2 years. Once he was released, he used his knowledge to make amends and became a white hat hacker. Mitnick died in 2023 from cancer.
Steve Wozniak

There are few people in the Western world today who haven’t heard of Steve Wozniak. Along with Steve Jobs, Wozniak helped build Apple. But before he had a hand in bringing us iPhones and MacBooks, Wozniak was a white hat hacker.
Wozniak was fascinated with how technology worked and wanted to understand it. One of the things he did was create “blue boxes,” which manipulated phone lines to give him free calls.
Dan Kaminsky

Dan Kaminsky is known for a discovery that, had he not uncovered it, could have adversely affected the entire internet.
Kaminsky discovered a serious flaw in the Domain Name System (DNS), a major component of the internet’s infrastructure. This flaw would have enabled cybercriminals to redirect people from a legitimate website to a malware-infested one. Thanks to Kaminsky, the flaw was patched, and disaster was averted. Kaminsky died in 2001.
Techniques and tools used by white hat hackers
So, what are the techniques and tools used by white hat hackers?
Techniques
- Penetration testing: This involves hackers putting themselves into the mindset of a black hat hacker and what they would likely do. Then, with the permission of the network owner, the white hat hacker will attempt to penetrate the network and list any security vulnerabilities they find so they can be repaired. Many white hat hackers make a good living doing solely this.
- Vulnerability scanning: Similar to penetration testing, vulnerability scanning is when the white hat hacker uses tools to scan networks for vulnerabilities, such as outdated software, weak passwords, and server misconfigurations.
- Social engineering: When a cybercriminal manipulates an insider and persuades them to give up important information like login credentials, it’s known as social engineering. Kevin Mitnick was fond of saying that the weakest link in any computer network was the people running it. Social engineering is proof of this.
Tools
Many hackers work using their own custom-made tools (which they don’t reveal to anyone else). But they may also use some of the following resources:
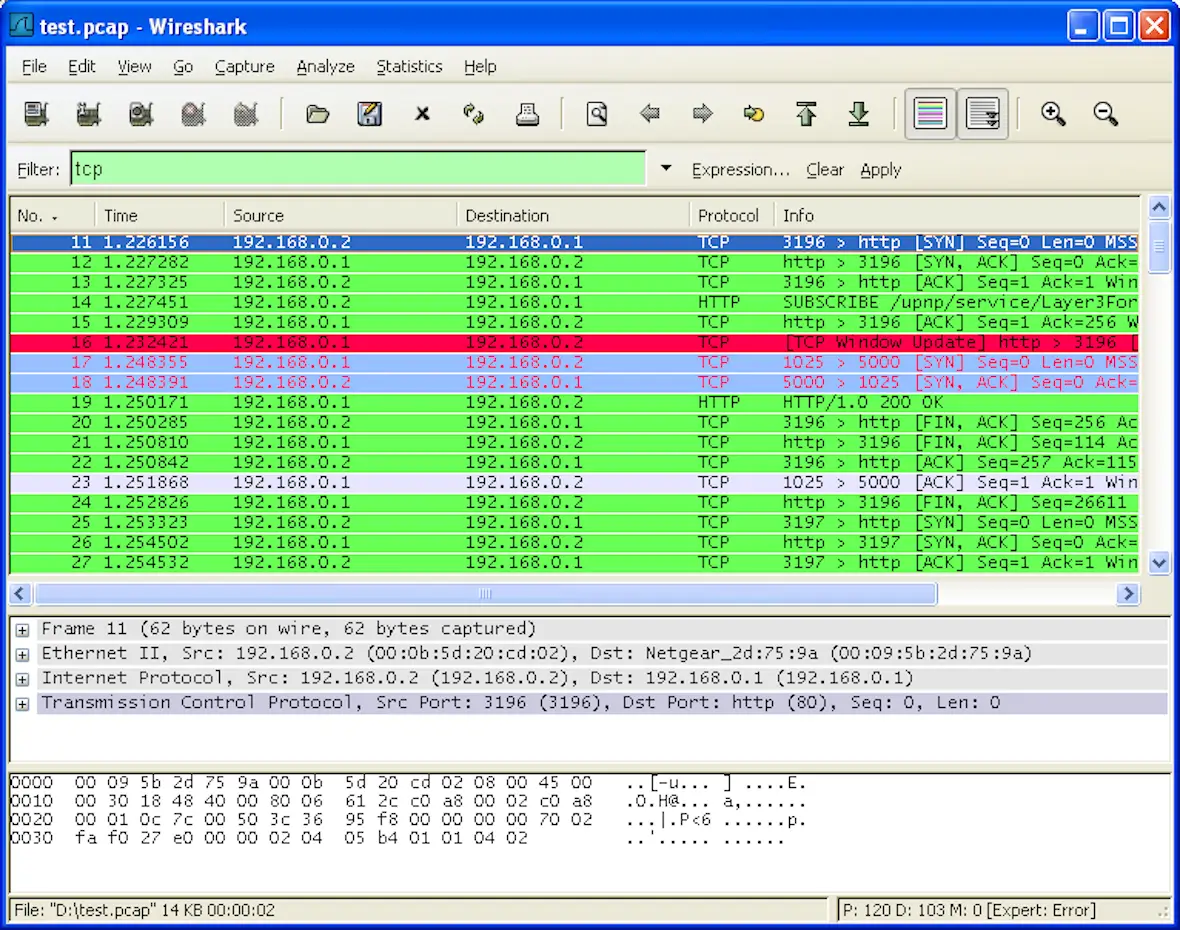
- Wireshark: Known as a “packet sniffing” tool (or by its proper name, a Network Protocol Analyzer, Wireshark is used by hackers to monitor networks and look for anything they can use, such as login names and passwords. It can be downloaded for free, as there are also many legitimate uses.
- John the Ripper: Similar to a tool called Hydra, John the Ripper is used to test the effectiveness of passwords by brute-forcing them. This means trying hundreds, maybe even thousands of combinations, until the password is found.
- Nmap: This is a tool used to scan networks to discover which hosts and services reside on that network.
- Burp Suite: The rather weirdly named Burp Suite is used to look for security vulnerabilities in web applications.
Black and white hat hacking: What are the differences?
The difference between a black and a white hat hacker is like night and day. Here are some of the main differences you can use to differentiate between them.
1. Motivation
In the end, intention and motivation make up the main difference between white and black hat hackers. Black hat hackers are criminals. Therefore, their motivations will be similar to the motivations of any criminal: financial gain, data theft, extortion, revenge, and more. Take the infamous Locky ransomware attack, for example, where black hat hackers extorted organizations for money by keeping their data hostage.
White hat hackers want to improve an organization’s or system’s security. Both types of hackers are highly competitive, and some white hat hackers may seek recognition. But the moral values of a white hat hacker are ethical and transparent. White hat hackers hack for global good or for a good cause, while black hat hackers have criminal and often personal motivations.
2. Legality
As mentioned, white hat hackers operate within the laws, while black hat hackers have malicious intent and knowingly breach these laws without any concern. The black hat hackers’ intentions are to steal, damage, harm, or conduct other activities that are illegal.
3. Anonymity
Cybercriminal organizations thrive in the shadows. To operate, they need anonymity. However, white hat hackers do not need to be anonymous. They can work while fully disclosing who they are, including the position, role, or job they’re doing.
4. Coding, testing, and malware
All hackers are sophisticated coders. However, white hat hackers do work that cybercriminals don’t do. This includes developing security software, tools, and techniques to detect and remove malware, pentesting (penetration testing), and building security patches.
On the other hand, black hat hackers are dedicated to coding malware and creating new social engineering techniques to trick users and breach systems. It could be said that while black hat hackers create problems, white hat hackers are creating the solutions. However, ethical hackers have lately taken on more offensive security approaches instead of preventive ones.
How to start your journey as an ethical hacker
If white hat hacking sounds like something you want to get involved in, here’s how you can go about it.
Become an expert in Linux
Hackers of any variety usually don’t ply their trade on Windows and Mac. Instead, most use Linux. So, the first step is to make yourself an expert in the Linux operating system.
Learn programming languages
Once you’ve got Linux down, it’s time to master programming languages. Python and Ruby are 2 good ones to know. You can get plenty of free online classes at places like Codecademy and Free Code Camp.
Teach yourself about cybersecurity
You can’t get involved in white hat hacking without a solid foundation in cybersecurity. Cryptography and risk assessment are a couple of good areas to start with.
Get a grasp on the concepts of network security
If you’re going to be poking through networks, you need to know how they work. Start with network protocols — DNS, FTP, HTTP, and SMTP, among others. Then, move on to routers, switches, and firewalls.
Essential skills and certifications for white hat hackers
If you’re going to be marketing yourself to potential clients, you should earn some certifications and training in the field. It shows that you know what you’re talking about. Some certifications and trainings to look into include:
- CompTIA Security+: This is a cybersecurity course and is more of an entry-level qualification. But if you’re serious about becoming a white-hat ethical hacker, you need to start someplace, and this is the best place to begin. Click here to find a location near you where you can take the exam.
- Certified Ethical Hacker: This is where you really start to get into the ethical hacking techniques and learn necessary skills like network scanning, social engineering, monitoring and hacking systems, and much more. You can take this exam at the same place as the CompTIA Security+ exam.
- Offensive Security Certified Professional: Its name may sound like it’ll teach you how to be obnoxious, but this course is when things get real. Complete this course, and you’ll be ready to start working as a white hat hacker. Learn Linux skills, get networks to hack into, and write detailed reports on it afterward. Click here for more information.
Where can you practice ethical hacking skills?
While training to become a hacker, you obviously can’t mess about with actual networks. So, where can you practice without causing the world’s stock markets to crash or unintentionally wreaking other types of havoc?
Luckily, there are 3 good online sources where you can tinker about to your heart’s content. Think of them as the Duolingo of ethical hacking:
- Hack The Box: This resource provides courses (or “labs”) of varying levels. Hack The Box gives you live virtual machines to try to penetrate.
- TryHackMe: As the name suggests, TryHackMe gives you a variety of targets to try to get into, as well as simulated networks to attack and defend.
- VulnHub: This one is slightly different. VulnHub gives you databases to hack into, but this one is a crypto wallet. You can download the database and attempt to break into it at your leisure.
White hat hackers contribute to innovation and security. The thrill of hacking and the challenge of building a better, more efficient, more inclusive digital world continues to feed the white hat culture just like it did in the early days.
As the world innovates with cloud computing, the edge, AI, 5G, machine learning, and IoT, a rich culture of hacking, seemingly lost for decades, has returned. In our highly digitalized world, every company and organization has a digital footprint. And when almost everyone has a digital life, data has never been so valuable.