Using digital resources every day means you must take extra precautions to keep your data safe. One way to do this is to use apps like WhatsApp that include end-to-end encryption to keep all your communications private and secure. But what is end-to-end encryption, anyway? In this article, we’ll examine what it is, how it works, and how it keeps users safe.
Understanding end-to-end encryption
End-to-end encryption (E2EE) means that no one can listen to any of your conversations or steal photos, messages, videos, documents, or anything else. In terms of WhatsApp, this applies when users are using the app. Only you and the other person can access your texts, calls, and shared info. It’s like speaking through a private tunnel with one person on each end.
Feel safer using WhatsApp with Moonlock
How do you define end-to-end encryption?
What is end-to-end encryption? By definition, end-to-end encryption means that your data is encrypted starting on your device. It then travels through the internet, encrypted, until it reaches the other party and their device decrypts it. All of this happens within milliseconds and is entirely invisible to the user. E2EE works on voice calls, text messages, video calls, and sharing information.
What does end-to-end encryption in WhatsApp really mean?
End-to-end encryption is the process of converting text or data into ciphertext (unreadable gibberish) to keep it safe from prying eyes and ears. Only authorized parties can use the data because each device shares the key that unlocks it.
WhatsApp end-to-end encryption keeps all your voice, text, and other data secure by converting it to ciphertext and back again instantly. During transport, no one else can access it except the two (or more) parties sharing it.
End-to-end encryption examples
Many companies and apps use end-to-end encryption to keep things private and safe. Some examples of how end-to-end encryption is currently used include:
- WhatsApp is an end-to-end encryption messenger that you can install on your iOS or Android phone to keep all your communications private. Using WhatsApp, you can make calls, text people, send photos and videos, and even share documents, all in a secure app that keeps intruders out.
- iPhone has built-in end-to-end encryption for text messages, calls, FaceTime, and email. Due to the iPhone’s patented system of tightly integrated software and hardware, they can seamlessly build encryption into the system.
- Telegram is another communications app that uses end-to-end encryption for all its functions to keep users’ data safe and private.
- Signal, another private messaging app, uses end-to-end encryption for calls, texts, and sharing securely.
- Google Messenger employs E2EE for security in its messaging system to keep users’ data and conversations private.
- Credit card processing systems use E2EE to protect cardholder names, credit card numbers, and passwords.
- Email platforms offer end-to-end encryption to protect your emails and any attachments from interception.
How end-to-end encryption works
Historically, end-to-end encryption was extraordinarily complex and difficult to use, even for highly skilled technicians. Modern technology makes it effortless for the end user, and dozens of apps come with E2EE built in.
The application you are using creates a secret key when you initiate a connection with someone. The app then scrambles all your data so no one outside your private conversation can understand it. The person on the other end shares that same key, which unlocks the data so they can communicate with you over a private connection. This is how all your personal messages are end-to-end encrypted.
Not only are phone calls, texts, and docs protected, but status updates are also end-to-end encrypted.
What does it protect against?
Keeping your online communications safe is essential to protecting your private information from identity theft. Hackers are always looking for ways to steal your personally identifiable information (PII), bank information, or credit card numbers.
Another way end-to-end encryption keeps you safe is by thwarting the government and technology companies from mining your personal information and tracking you. Marketers also harvest information for targeted advertising, but E2EE can help protect you against that, too.
Secure email allows you to send things like W2s or other legal documents with your social security number, driver’s license, or passport number on them without worrying that some hacker will intercept them and steal your private data.
Man-in-the-middle attacks are when someone intercepts your online communications to spy on you or steal information or money. Fortunately, E2EE protects you from these types of attacks and other hacking incidents. If hackers can’t find you, they can’t affect you.
How is end-to-end encryption different from encryption in transit?
Some people confuse end-to-end encryption with encryption in transit, but they are two very different things.
Encryption in transit means that data is only encrypted during one leg of its journey and may be vulnerable at the other end or during transit somewhere over the network. End-to-end encryption is when data is encrypted the entire time it is online. It is never exposed to outsiders and, therefore, is much more secure.
Is WhatsApp encrypted?
WhatsApp conversations are encrypted for all users with end-to-end encryption. Only the sender and receiver can read each other’s messages. The only part that is not encrypted is the metadata, which can be seen by WhatsApp.
This metadata includes information such as the time the user sent the message and who the message was sent to. The contents of the message, however, remain unseen.
Are WhatsApp calls encrypted?
Just like WhatsApp text messages, WhatsApp calls are encrypted using the same end-to-end encryption to prevent anyone from listening to the phone conversation.
It is not known whether or not law enforcement has ways to circumvent end-to-end encryption. However, unless you are someone engaging in serious criminal activity, it is unlikely that they are listening.
How WhatsApp uses encryption to secure chats
We’ve already covered how end-to-end encryption works, along with some examples of it in action. WhatsApp’s end-to-end encryption means that there’s no chance for someone to intercept a message between the sender and the receiver, nor can they view or hear the conversation.
Here’s how end-to-end encryption works on WhatsApp:
- When one party begins the conversation, their device and the device receiving the message generate unique cryptographic keys. This forms the backbone of the encryption. They are generated in the background, so this is something the user doesn’t see.
- When you send a message, WhatsApp immediately encrypts it with your key and then sends it to the other person. This is done quickly in the background.
- When the other person replies, the same happens on their device. The message is encrypted with their key and sent to your device.
And so it goes on until the conversation is finished.
As previously mentioned, it should be noted that the conversation’s metadata is not encrypted. The metadata, which can be seen by WhatsApp, includes the date and time of the conversation, how long the conversation took, and who you were talking to. But the contents of the conversation will always be locked down and encrypted.
How secure is WhatsApp encryption?
WhatsApp’s end-to-end encryption is based on a protocol known as Signal. This is the protocol used by the heavily encrypted Signal chat app. It is considered to be extremely secure and all but impossible to crack.
The encryption generates unique keys to encrypt and decrypt messages that you send and receive. These keys are unique, as they are only used once and then discarded. The next conversation will get completely new keys.
How to enable or disable end-to-end encryption for WhatsApp chat backups
You don’t have to do anything to enable end-to-end encryption in WhatsApp. WhatsApp enables end-to-end encryption by default, and it cannot be turned off.
If you decide to enable the backup feature, your WhatsApp chats will be bundled up and sent to your iCloud account. WhatsApp encrypts the backups, so even if someone were to gain access to your iCloud account, they would have the same issues decrypting your WhatsApp chats.
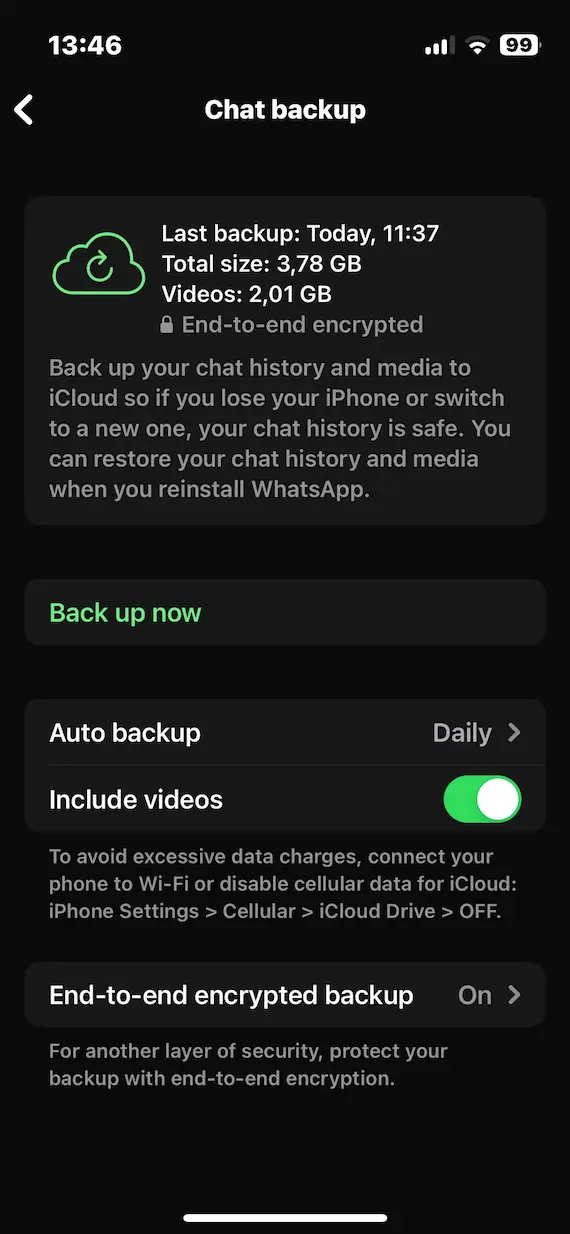

Nevertheless, you should ensure that your iCloud account has a secure password and 2-step authentication enabled. If you want to be extra careful, you can disable the backup option altogether.
Does end-to-end encryption in WhatsApp mean it’s 100% private?
WhatsApp, Telegram, and Signal are known for their strict encryption protocols and are considered ideal platforms for private conversations. However, that doesn’t mean that WhatsApp and other services are 100% private or safe. They still may be subject to certain types of threats.
Due to some inherent weaknesses within the app, independent researchers were able to hack more than 1,400 WhatsApp accounts. Hackers were able to use NSO spyware to access audio, video, photos, contact lists, location data, and more from WhatsApp users.
Someone with access to the receiving device could also read your texts and messages or listen in on calls. A stranger could also record your video calls.
Also worth noting is that WhatsApp has historically shared its users’ data (phone numbers, device data, etc.) with Facebook, which could be exposed to other parties.
Any communications platform is going to be vulnerable to threats. And although end-to-end encryption is a great tool and helps keep you safe, users must still use common sense. Do your own research and take preventive actions to keep all your data and communications secure.
This is an independent publication, and it has not been authorized, sponsored, or otherwise approved by Meta Platforms Inc. WhatsApp is a trademark of Meta Platforms Inc.