A VPN, also known as a virtual private network, is a powerful tool that can hide your location and protect you from various cybersecurity threats. Historically, VPNs were used exclusively when connecting to a workplace. Now, internet users of all kinds benefit from this added layer of security when using the internet.
VPNs may sound mysterious, but they are really quite simple, and if you aren’t using one, you should be. Let this guide help you understand what a VPN is, how to use a VPN, and why it benefits you.
What is a VPN, or a virtual private network?
To define a VPN, a virtual private network is a service that encrypts all your online activity, keeping it safe and confidential. A VPN starts with an app or program that you turn on. It then connects to a remote server, providing you with protection against intruders and online attacks. While the VPN is turned on, all your data is encrypted.
What is the meaning of a VPN?
A VPN extends your home or office network to other locations by creating an encrypted tunnel that is hidden and inaccessible to anyone other than you. All your data is encrypted from your device to the connected server or application you are using. It’s like driving through an underwater tunnel. You’re safe and sound inside the tunnel while the danger stays outside.
What does a VPN do?
One of the most commonly asked questions about VPNs is, “What is a VPN, and what does it do, anyway?”
Anytime you browse the internet or use applications on your phone, you’re not just making a quick, direct connection. Rather, requests travel from your device to a remote location by making a few stops along the way, bouncing off many remote servers. During this journey, bad actors who want to steal your information or money can sabotage or intercept it.
A VPN, on the other hand, connects you directly to a highly secure server, which routes your traffic to your final destination through an encrypted connection.
The VPN hides your IP address and assigns you one from a remote location so that hackers cannot determine your exact location or IP and break into your private network.
How exactly does a VPN work, and why should you care?
As earlier stated, a VPN protects your privacy by relaying your internet browsing through its own private network of worldwide servers. When you browse without a VPN, your IP address is logged as having visited a particular website. This makes it very easy to trace you or to track you for advertising purposes.
When you use a VPN, your IP address is concealed, as everything you do online is redirected through the VPN. This makes it virtually impossible for you to be tracked or traced since VPN providers don’t keep user logs indicating your identity or location.
While it is absolutely critical to use a VPN, all VPNs are not created equal. Moonlock’s VPN, designed specifically for Mac, gives you full protection and a completely encrypted connection. Its VPN is built into the software, and it makes sure that your IP address stays private, your traffic is encrypted, and all of your data is kept locked away, no matter if you are on public Wi-Fi or at home. Combine this with AES-256 encryption, a transparent no-logs policy, and a Kill Switch to keep your peace of mind completely intact.
Moonlock is more than just a VPN. It is a complete Mac protection tool that includes a Malware Scanner, System Protection, 24/7 real-time protection, and background monitoring to constantly protect your Mac from all angles. And the best thing is, you can try it for free and see how it works.
Types of VPN connections
The term VPN is broad and covers many different types of VPN connections, some of which you may have heard of, and others may be new to you. Here are the most common types of VPN connections.

Remote access
A remote access VPN is a closed connection, usually between an employer and an employee. The purpose is so that the employee can log on security to the company’s server and access all its resources remotely. This type of VPN can help tremendously when traveling abroad, where some websites might be blocked.
Cloud VPN
A cloud VPN safely connects users to a cloud environment over the internet. An excellent example is Amazon Web Services (AWS) or Microsoft Azure.
Site-to-site VPN
A site-to-site VPN is a single, direct connection between two routers, often used by large corporations to connect satellite offices. They include both intranets and extranets.
Mobile VPN
A mobile VPN works on a mobile device, allowing the user to securely connect to a private network or use internet resources safely. Typically, the user installs an app on their phone and then connects through their wireless network.
SSL VPN
An SSL VPN (secure sockets layer virtual private network) uses an SSL protocol to secure the connection between the user and the network. Web services employ SSL connections by encrypting all data that passes through the website, keeping users safe.
PPTP (Point-to-Point Tunneling Protocol) VPN
The PPTP VPN is one of the oldest and simplest forms of security. It encapsulates data packets sent between two computers and secures them. It doesn’t require any special hardware or software but is considered less secure than other VPNs.
L2TP (Layer 2 Tunneling Protocol) VPN
L2TP is an advanced form of PPTP with an additional layer of security and a robust encryption algorithm.
Open VPN
OpenVPN is an open-source application that also encapsulates data between two computers. It’s highly flexible and secure, allowing users to securely access databases, email, and websites.
Why do you need a VPN, and why should you use one?
Today’s modern, digitally focused world requires us to use online resources for almost everything. You cannot be safe enough online. A VPN can help keep all your information safe and secure and give you peace of mind that your online activities will remain private, as they should. Here are some of the benefits of using a VPN.
Use public Wi-Fi safely
Logging on to a public Wi-Fi network at your local coffee shop, the airport, or a hotel is unsafe unless you use a VPN. Hackers often use unsecured Wi-Fi to commit man-in-the-middle attacks.
With a VPN, you could sit at Starbucks sipping your latte safely and log onto your bank account without worrying about anyone stealing your credentials.
Mask your IP and location
Cybercriminals can use your IP address to break into your home network and wreak havoc on your life. A VPN masks your IP address and makes it appear that you are logging on from a completely different location, so hackers cannot track you.
Anonymous browsing
It seems like everyone is tracking everyone online these days for marketing and other purposes. With a VPN, you can browse the internet anonymously without worrying about who is spying on you.
Avoid content restrictions
Some countries block access to things like Netflix and other streaming services. Even when you travel, you can use your VPN to connect to and use these services without interruption.
Avoid identity theft
VPNs give you an extra layer of security to keep all your private information safe and secure, no matter where you browse or what games or apps you use. They can also help you avoid nasty cases of identity theft, which are tricky to bounce back from.
How do you use a VPN to protect your online activity?
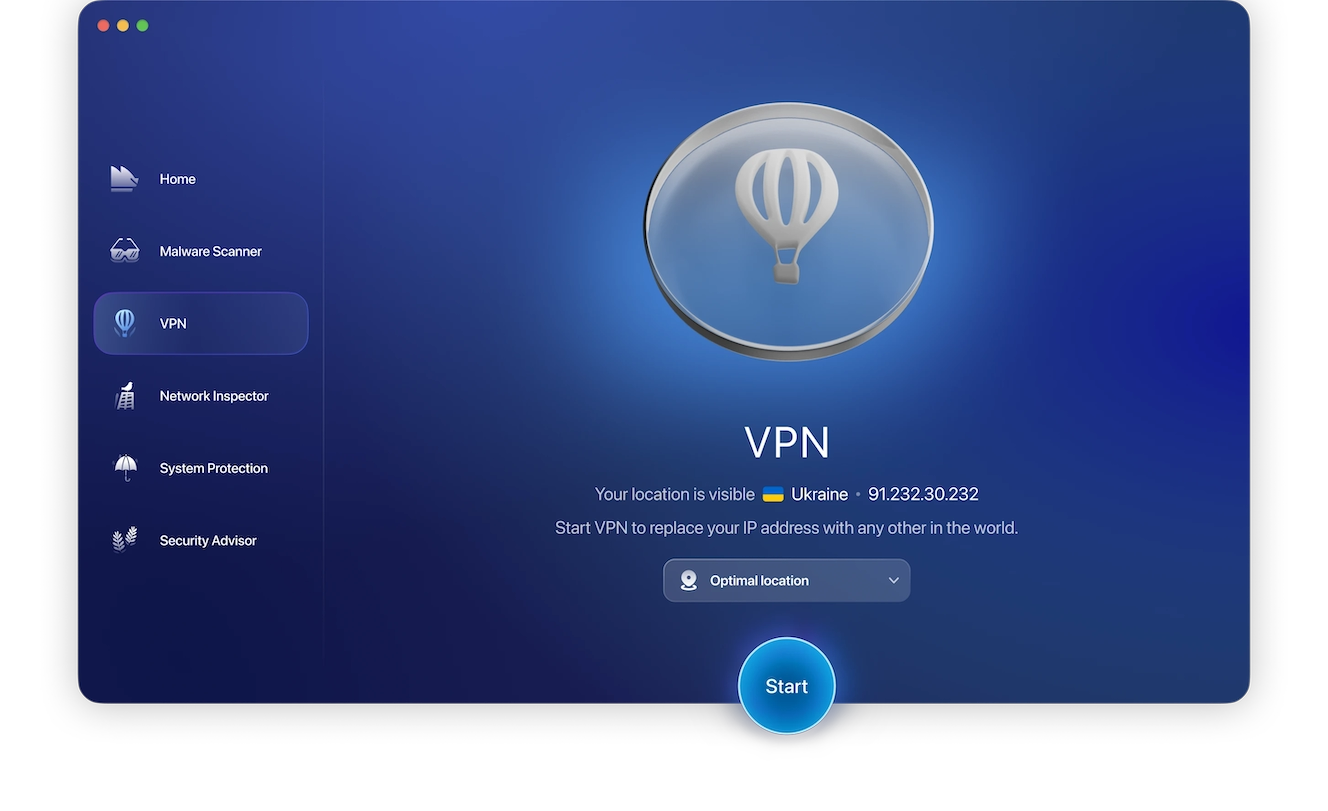
When you install a VPN such as Moonlock’s VPN, you will need to also install some configuration files on your Mac to make it connect properly. From there, it is a simple case of selecting which country’s servers you want to connect to (this is good if you need a particular country for streaming).
If you are not fussed about where you connect to, Moonlock’s VPN will automatically connect to an optimal location. This is usually the closest server to your current location.
Once you’ve selected a server, you may then have to refresh any web pages you’re on or apps you’re using to see the new version for the location you selected.
How do you set up a VPN for secure browsing?
Getting set up with a new VPN doesn’t have to be overly complex, and Moonlock makes it as simple as it could possibly be. The VPN is completely built into the software and can be enabled almost immediately.
Here’s how to protect your privacy in seconds with Moonlock’s VPN:
- Start your free trial of Moonlock and open the software.
- Go to the VPN tab.
- Click Connect to instantly encrypt your traffic and hide your IP address. You can go into the settings here and choose the location and server of your choice for more personalization.
- Make sure to enable real-time protection and background monitoring in Moonlock to keep your Mac protected 24/7.
How do you change your VPN location?
Assuming you have the Kill Switch enabled, you can very easily bounce from one server to another while staying protected at all times. It’s like going on a round-the-world trip and never leaving your sofa.
The true beauty is that because connecting to a server is usually quite fast, you don’t have to worry about your internet connection blinking out too often.
Here’s how to change your VPN location:
- Open Moonlock’s VPN. Your VPN runs constantly in the background, but opening the VPN tab will get you into the interface to see the current server location.
- Choose the region or country of your choice.
- Hit Connect. This will instantly switch to the new location with no lag in protection.
Change your virtual location and stay protected anywhere with Moonlock’s VPN.
How do you turn off your VPN?
Turning off your VPN is as simple as clicking a button. In Moonlock’s VPN, for example, the big round connection button in the middle of the app screen will turn off the connection with a single click or tap. Turning it back on again is just as easy.
Note that it is possible that a VPN will still have some background tasks running even if you have disabled the VPN itself. If this is the case, you can shut them down manually via Mac’s Activity Monitor.
How do you check if your VPN is working properly?
When you have switched on your VPN, how do you know if it is actually working properly? There are several things to watch out for:
- Is your VPN app showing the new country with a timer counting the connection time?
- Are websites showing a country-specific page?
- Are streaming platforms working? For example, BBC iPlayer will only work if you are connected to a British server.
- Has your IP address changed? You can check it by going to a website such as What is my IP? You can see at a glance where your computer connection is at.
VPN troubleshooting and usage FAQs
If you have any further questions regarding VPNs, we have tried to cover them below.
Why isn’t my VPN connecting?
If your VPN isn’t connecting, the first thing to check is if your router is working optimally. If not, restart it. Second, have you entered the correct login details into the VPN? Third, it’s possible that too many people are using the selected server. Try moving to another one. Finally, restarting the VPN may be all you need to do.
Will using a VPN slow down my internet speed?
Using a VPN can slow down your internet connection. The degree to which your connection speed is affected will depend greatly on the server you choose. The closer the VPN server is to your location, the faster your internet speed will be. If you choose a server on the other side of the world, your connection speed will decline as a result.
Are VPNs legal to use?
Yes, VPNs are completely legal to use. There are instances where governments and law enforcement agencies have a harder time tracking down criminals due to VPN usage. Additionally, streaming services dislike the fact that users can bypass their location-specific content restrictions by using VPNs. Nevertheless, using a VPN is completely legal.
Is it safe to use a VPN for browsing?
Yes, it is safe to use a VPN. If you enable the Kill Switch, your location will still be protected. Your web activity will be heavily encrypted. Plus, VPN companies do not store logs of user data, payment details, or the websites their users have visited. They may keep connection logs, which only show how many times you connected to the VPN. However, many VPN companies these days are choosing not to even keep these.
What is a double VPN, and how does it work?
A double VPN is when your internet traffic goes through a VPN server, and then the VPN server sends it through a second VPN server. This guarantees extra privacy and protection.
Although the first VPN takes your data and encrypts it, the second VPN will only receive the encrypted data from the first one. By the time it passes through the second VPN, the data is completely anonymized. Not surprisingly, the speed of your connection will drop a bit more as a result.
Can a VPN be tracked by anyone?
A VPN just makes it a great deal harder for anyone to track you, but nothing is infallible. There are extremely rare circumstances when VPN traffic can be tracked by government or law enforcement agencies with the right tools and resources at their disposal.
Some misconfigured VPNs can suffer from DNS leaks, where the curtain is temporarily lifted to reveal your real IP address. Metadata on a connection log, such as the time you connected and the duration of the connection, can also be used to connect the dots and make assumptions about you.
You can mitigate these risks by always keeping the Kill Switch on, using a double VPN if your VPN provider offers it, and always choosing a top-quality VPN, such as Moonlock’s VPN.
VPNs are another valuable resource in your cybersecurity toolbox that you can use to stay safe. They are inexpensive and easy to set up and use. Most importantly, the added protection they give your information online is priceless.