Online privacy is on everyone’s mind these days. However, our modern digital world is making privacy much more of a challenge to achieve. The internet and shared networks open up untold vulnerabilities, and many of us are unaware of the extreme dangers. One of these threats is spyware.
Keep reading to learn what spyware is, how it works, and why it’s so dangerous. Find out what kinds of spyware are lurking online, how to remove spyware from your device, and how to protect yourself from future attacks.
What exactly is spyware?
Spyware is a very broad term that covers tools used to secretly gather and steal information from a computer or other digital device. This is done without the consent of the device’s owner and may be carried out by a hacker, a cybercriminal, or a government agency.
Most victims are targeted by garden variety criminals, but their methods of planting spyware on target computers are evolving and getting more advanced all the time. Computer spyware can include things like keyloggers. They can also track the sites you visit, take screenshots, and capture the login details for your online accounts.
There are ways to spot spyware software if you know what you’re looking for, and removing it is usually a straightforward process, unless you are indeed being watched by a government agency. Then the chances of detecting and removing it are very slim.
What spyware does and how it works
At a basic level, spyware works very simply and uses a variety of methods to enter a target computer. It can breach a computer via phishing emails, free software, infected email attachments, downloads from shady websites, infected USB drives, and fake software updates.
Here is the usual process for what spyware does once it’s on your system:
- If the spyware includes a keylogger, it begins to log everything you do on your keyboard. Every key touched gets logged, which means account login details are captured, as well as chat message transcripts and search queries. It can track what websites you go to and gather credit card details, PIN numbers, and much more.
- Spyware can also take screenshots of your computer screen, which enables bad actors to steal sensitive and compromising pictures.
- Spyware can take over your camera and microphone, so you can be watched and listened to. This is often done without your knowledge, as the camera’s indicator light will usually be disabled.
- It will begin to sort through your documents, your clipboard, and your system files. Any files worth taking will be remotely transferred to an outside server. They may encrypt those files to avoid triggering firewall alerts.
Spyware usually modifies your system files and startup process, so it begins as soon as you log in. It can also hide inside legitimate programs to make it more difficult to detect.
Why is spyware so dangerous?
When used as malware, spyware is highly dangerous because the perpetrator can gain access to your most sensitive and personal data, leaking it on the dark web for financial gain. This type of threat often leads to identity theft, which is an awful experience. Shockingly, spyware can also disconnect some antivirus software, making it virtually undetectable.

Are Macs and iPhones vulnerable to spyware malware?
It is slightly more difficult for an attacker to place malware on a Mac or an iPhone than it is to do so on Windows devices. But it is indeed possible. Anyone who tells you differently is either operating with outdated information or is being naive. With the number of macOS and iOS users on the rise, cybercriminals cannot afford to ignore these platforms.
The difficulty for criminals lies in the way macOS and iPhone devices are built. System files are segregated into their own compartments, and each one is isolated from the rest. This makes it very difficult for malware to spread.
Add to that the spyware protection tools inside a Mac. These are features like Gatekeeper (which stops all non-App Store downloads from coming in), XProtect (Mac’s built-in malware scanner), and System Integrity Protection (SIP), which prevents core system files from being altered.
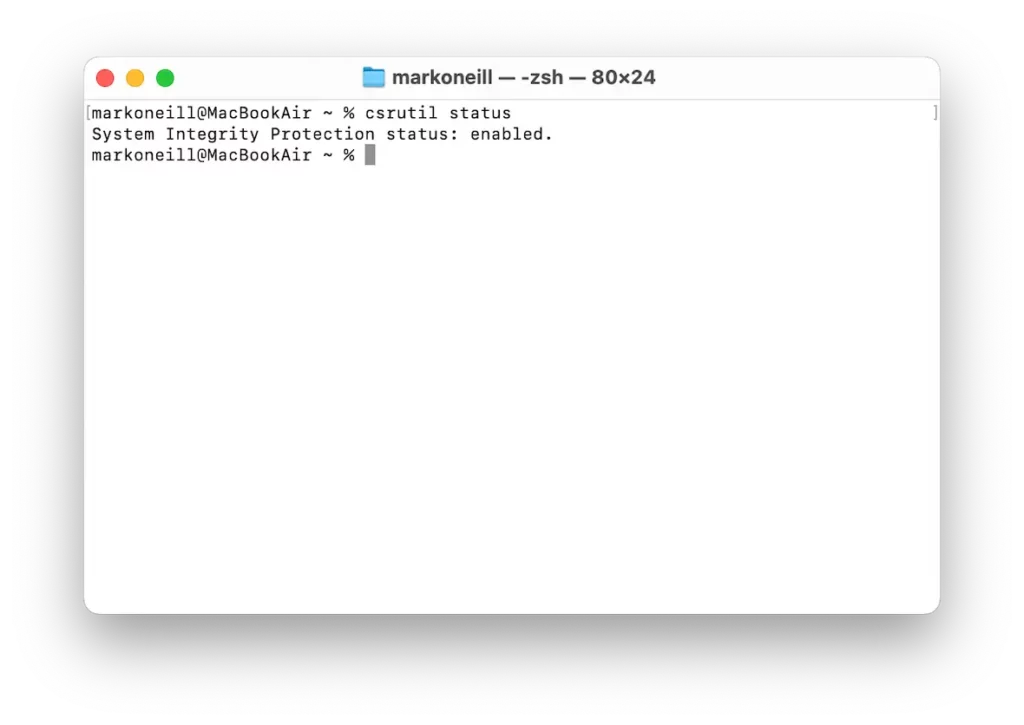
But spyware on Mac still manages to happen, as well as, to a lesser extent, on iOS. Here’s how:
- Many people disable Gatekeeper to get their favorite non-App Store downloads onto their device.
- Malware is often accompanied by legitimate developer certificates to bypass Gatekeeper.
- Malware inside a zip file downloaded to your Mac won’t get stopped by Gatekeeper.
- If the malware is a zero-day exploit, XProtect may not have it in its database yet.
- System Integrity Protection doesn’t cover directories like Library, which is a favorite hiding place for malware.
- Some malware lies dormant until the victim clicks a fake notification asking them to enter their administrator password.
- Despite all of Apple’s security tools, the easiest way to infiltrate someone’s computer is by preying on the user’s trustworthiness. Social engineering techniques like fake antivirus warnings and fake Adobe Flash updates are things that many people accept without questioning them.
When it comes to spyware on iPhones, it is also slightly more difficult to hack, but mobile spyware is still possible. This is due to frequent security updates, a ban on sideloading, and sandboxing.
However, it does happen. Here’s how:
- Governments have been known for the infamous Pegasus spyware, which was spread through Messages and WhatsApp.
- Commercial spyware is easily obtainable for jealous exes, stalkers, and parents. All they need is the phone owner’s iCloud details (and sometimes not even that).
- Phishing links sent via Messages, WhatsApp, and emails can change the phone’s configuration profile, change DNS settings, and install apps.
- Apple’s App Store has a near-perfect record for keeping out infected apps, but the system isn’t perfect. There have been 1 or 2 occasions where rogue apps have managed to slip through the net.
- Charging your phone using an unknown charging port can send malware to your phone via the charging port.
- Although it is highly discouraged by Apple, people also still jailbreak their iPhones and sideload unofficial apps. This collapses all security protocols and invites malware through the front door.
Who wants to install spyware on your device and why?
So, where does spyware malware come from? There are many categories of spyware owners, and they all have their individual motives.
Hackers and cybercriminals
This is arguably the biggest group of offenders, and their motive is always money. They will go after your crypto wallets, bank account details, PayPal, credit card details, email or social media, and your files.
Government agencies
If you are unfortunate enough (or notorious enough) to warrant the attention of a government agency, then they, too, can place spyware on your devices. Their motives are purely to monitor your activities and determine whether or not you are a threat. They may also copy and view your files, emails, and search history for the same purpose.
Spyware from government agencies is usually highly advanced compared to the kinds used by criminals. Therefore, if you’re being monitored, it can be impossible to know without access to advanced tools and knowledge.
Parents, suspicious partners, and stalkers
Spyware can also be freely available online for anyone to be “monitored.” This is usually marketed as software to be used by a parent to monitor their child. But, of course, it can be repurposed by others to spy on whomever they want.
Employers
Like the last category, spyware can also easily be bought for employers to monitor their employees to “optimize productivity” and “identify bottlenecks.” Needless to say, it can also be used to spy on employee emails, chat history, and personal data.
How to get rid of spyware on your Mac
If you’re particularly tech-savvy or like to take matters into your own hands, you can definitely try and get rid of spyware manually, but be warned that the process can be cumbersome. Not to mention, you might not be able to remove all of it, leaving you vulnerable to future snooping.
The best way to reliably remove spyware from your device is by using a dedicated antimalware tool designed for Mac, and Moonlock is one of the best and easiest to use tools out there. Just follow these simple steps:
- Sign up for your free trial and download Moonlock.
- Open the app.
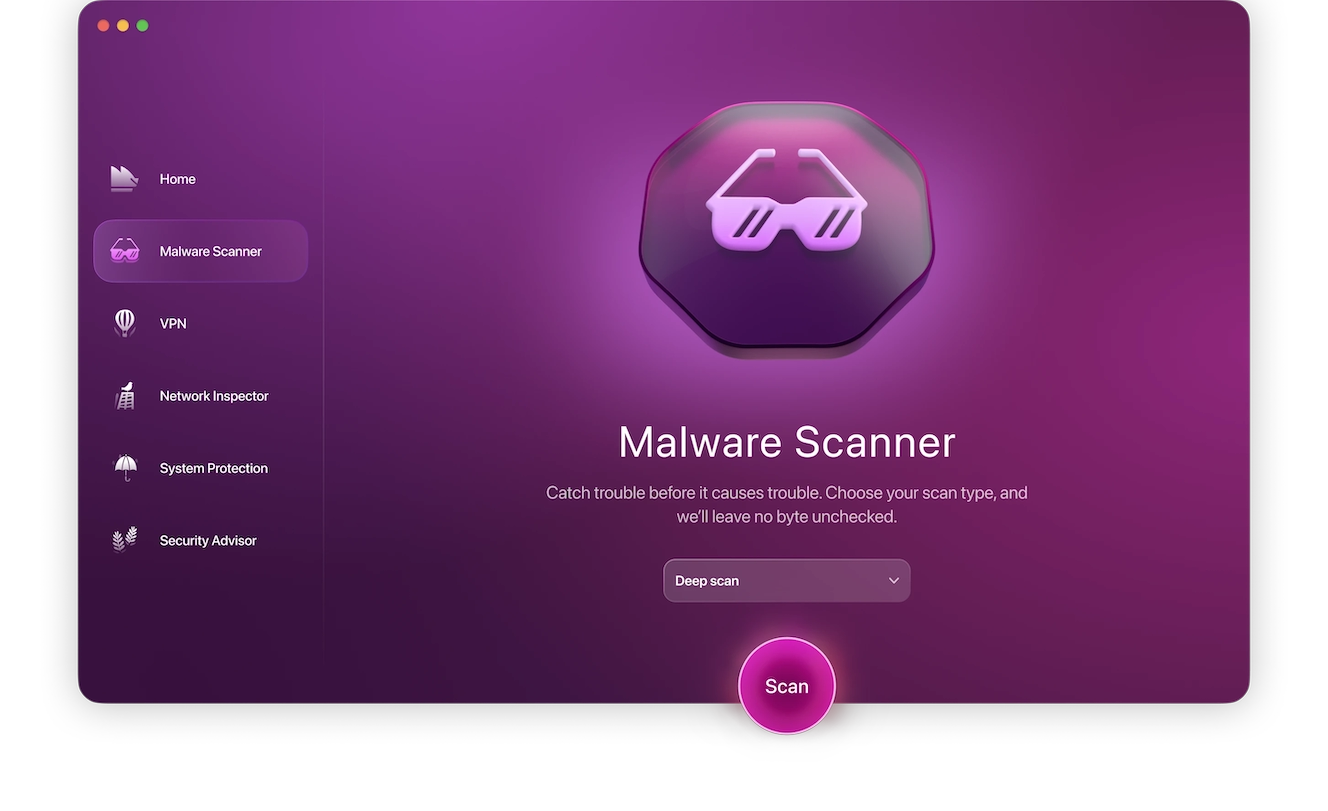
- Click Malware Scanner from the left side navigation bar.
- From the drop menu, choose between a Quick, Balanced, and Deep scan.
- Click Scan.
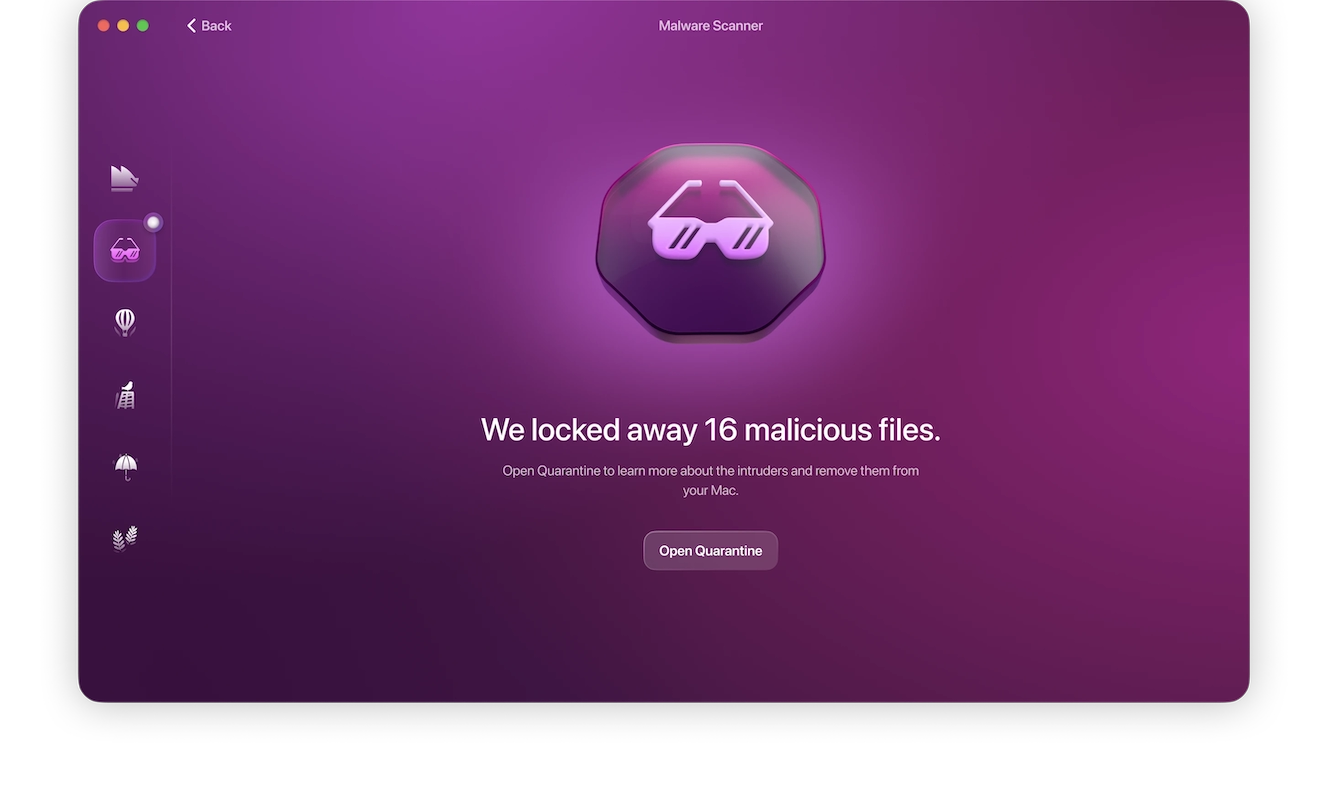
Moonlock will then proceed to inspect your Mac, looking for anything suspicious, whether it’s malware, spyware, or vulnerabilities in your settings configuration. If Moonlock finds spyware on your device, it’ll immediately move it into Quarantine, where it won’t be able to snoop through your files anymore, before it deletes it.
Types of spyware
There are many types of spyware to be aware of and watch out for. Each variety has its own distinct characteristics and methods of operation. Some are simply nuisances, but others are far more dangerous.
Adware
Adware infiltrates your device and tracks your online activities to feed you pop-up ads at inconvenient times. It may also sell your information to marketing companies to help them tailor custom ads to you based on your preferences.
Keyloggers
Keyloggers can be very dangerous. They log every keystroke you make, so when you log on to your bank or credit card accounts, the spyware tracks the keys you press when entering your username and password. Keyloggers are insidious and meant to steal your login credentials and drain your accounts.
Trojans
Trojans are pieces of malware that come packed with other seemingly legitimate software. Hackers piggyback spyware payloads onto free software that, when you install it, you get a nasty bonus.
Rootkit
Rootkit malware installs a backdoor so that hackers can enter a network or device any time they like. Using this type of spyware, attackers can take complete control of the system and take what they want.
Red Shell spyware
Red Shell spyware is a platform designed to collect massive amounts of data about its target. Red Shell is very dangerous and used mainly in network takeovers and large ransomware attacks.
Cookie trackers
Cookie trackers leave tiny breadcrumbs in your system so that other types of malware can detect the information stored there. Cookies collect data about preferences and online activities. Usually harmless, this type of spyware can be damaging and track you across the internet.
Real-life examples of spyware attacks
The best way to describe a spyware attack is to cite recent examples and the effects they have on the victims. Some notable real-life examples of spyware attacks include the following.
Pegasus
The Pegasus spyware debacle was all over the news in 2021. The Israel-based NSO Group’s Pegasus spyware was found on the phones of political activists, media moguls, journalists, and workers within companies who were clients of NSO Group.
Ghost RAT
Also in 2021, NoxPlayer (a free Android game emulator) was discovered to be laced with spyware capable of remotely controlling a user’s device. Hackers infiltrated BigNox, the game emulator’s developer, and piggybacked their own software in a trojan horse attack.
PhoneSpy
Later in 2021, cybersecurity experts discovered a spyware app in South Korea affecting Android devices. The program pretends to be legitimate software while it collects data and remotely controls the device. Around 1,000 devices were affected.
How to protect yourself from spyware
The best way to avoid the effects of spyware and protect your devices and network is to never let it in the door in the first place. Follow these cybersecurity best practices to stay safe.
Avoid dangerous downloads
Never download free software unless you know it’s entirely virus/malware-free. Stick to downloading apps from verified sources such as the App Store, which employs a rigorous safety protocol to ensure that all the software on its platform is legitimate.
Never click on links in email or SMS
Do not click on links in email or SMS messages, especially if you don’t know who sent them. Be particularly cautious of messages with a sense of urgency that make you feel panicked. Phishing scams are designed to make you click without thinking.
Always rely on solid antivirus/antimalware software
Don’t wager your privacy or the health of your device on just any antivirus out there. You need a tool you can count on to always have your back, from the simplest adware to downright dangerous malware and spyware.
Moonlock doesn’t just clean your device when it’s infected. It stops malicious software at the door with round-the-clock background monitoring and a Security Advisor to help you take control of your online experience.
Keep software/hardware updated
Keep your software (apps and operating system) and your hardware updated with the latest security patches and firmware to keep the bad guys out.
Spyware is just another notch in a hacker’s belt and one method of committing fraud and theft. As long as you know the threats, you can prepare yourself. Watch out for the dangers to keep you and your data safe.