There are many types of malware out there, but one of the most destructive types can self-duplicate and jump from network to network. Highly favoured by cybercriminals, this malware can be extremely difficult to locate. It’s called a computer worm. It’s one of the most insidious examples of malware out there, and it’s only getting worse.
Computer worm: The definition and how it works
Worms in cybersecurity have been responsible for some of the most high-profile and most damaging cybersecurity incidents in the world, with examples including ILOVEYOU, Code Red, and Stuxnet.
Many pieces of malware need an app in order to do their job. Worm malware, on the other hand, requires no such handholding. Once released into the wild, this highly dangerous virus will breed and duplicate rapidly, spreading to as many computer networks as possible. This means that once it’s out there, it’s virtually unstoppable.
Since its invention in 1987, the computer worm has evolved. It’s estimated that there are over a million active worms out in the world today, causing damage and general havoc to networks.
On the one hand, they steal data and delete important files. On the other hand, they are also frequently used by governments to launch cyberattacks against their enemies and cause systems to break down.
Stuxnet is a classic example of a worm attack, when computers controlling Iranian nuclear centrifuges were attacked. It’s widely believed that Israel was behind the attacks.
Once a worm is on the target computer, its aim is to take advantage of unpatched vulnerabilities in software or operating systems and then to multiply, steal data, and generally cause chaos.
How computer worms work
Worms scan internet networks in search of computers, smartphones, and tablets with specific vulnerabilities they can exploit. The worms then use these vulnerabilities, usually found in operating systems, as doors into computers, mobile devices, and tablets.
Once a worm has set foot inside a computer or device, it will self-replicate and continue moving on. The copy it leaves behind is then activated. And depending on what it was coded to do, it may steal sensitive data, change system settings, send information, launch bulk messaging or email campaigns, and more. The process of the worm cloning itself, spreading, and launching attacks is instant.
What makes worms even more dangerous is that they require no action on the part of the victim. Contrary to viruses or other malware, which must trick users into taking a specific action (clicking on a link or downloading a file), worms are able to spread independently. Worms also work in stealth mode in the background.
In the old days, hackers would infect computers with worms by gaining physical access. This meant they had to get up close to the computer and insert a floppy disc or other types of media into the computer’s drive. But today, worms spread using different techniques.
How do worms spread today? The most common methods worms use to spread include:
- Email (phishing or spam)
- SMS messages
- Through network scans
- Messaging apps like WhatsApp or Messenger
- File sharing sites
- External media devices include USB, memory cards, and external hard drives
Frequently asked questions about computer worms
Yes. Worms can infect all types of smartphones. Some, known as mobile worms, are specifically designed to target mobile devices. These can breach a device through a malicious file, email, SMS, messaging app, or network.
Many worms still spread today through USB media. Cybercriminals may insert the worm into the USB, or a worm on a computer may infect a clean USB. Because worms are self-contained, USB spreading is automatic and requires no action from the victim.
A worm can go global in just minutes, spread, and infect hundreds of thousands of computers, including devices at high-level organizations such as governments with cutting-edge cyber security technology.
As previously mentioned, worms are designed to instantly infect, spread, and activate. The speed at which a worm can spread will depend on how efficiently coded it is and the resources and power of infected computers and devices. Worm attacks can last a couple of hours before experts find the kill switch.
Yes, a worm can contain a virus or other malware, such as ransomware or spyware. Worms can also open backdoors for malware to be easily installed on a computer or device.
Types of computer worms
There are many types of computer worms out there, each targeting a different computer component. Let’s run down the list of each one:
- Zero-Day – the notorious Stuxnet worm finds unpatched security vulnerabilities in operating systems and software. The term “zero-day” refers to these vulnerabilities, which are as yet unknown to the vendors, and therefore, no patch is actively being developed yet. Zero-day worms are usually deployed by countries against high-profile targets.
- Bot worms – this is an example of a double-whammy, where the first worm brings with it a second piece of malware. This could be adware, ransomware, remote access trojans, forming a botnet, and many others. An example of a botnet is Conficker, which created a massive botnet against Windows computers.
- Mobile worms – the name explains the target. Mobile worms go after smartphones, usually through SMS links, malicious apps, and Bluetooth. One type of mobile worm was Cabir. Its mode of transport was Bluetooth.
- File-sharing worms – these worms are a classic example of why you should be wary of P2P networks. Worms embedded in cracked software will jump onto target computers as soon as the software is installed. One type of file-sharing worm is Mytob, which was (and perhaps still is) all over file-sharing networks.
- Email worms – this one targets emails with phishing links and infected attachments. These worms represent the type with the highest rate of effectiveness, as people still click links from unknown senders and download attachments. This was what the ILOVEYOU virus was.
- Internet worms – internet worms scan systems and servers for unpatched vulnerabilities. A classic example of a network worm is Code Red, which attacked Microsoft servers in 2001.
Symptoms of a computer worm
While worms are very good at hiding, there are several symptoms you may experience that should immediately raise red flags.
Worm symptoms include:
- Your computer is slow or crashing: Worms feed off the resources of your device, such as memory, RAM, and hard drive space, and are very active and aggressive. This activity tends to slow down computers and smartphones, make them act up or behave strangely, and even crash.
- You are out of storage space: If you get warnings that your smartphone or personal computer is running out of space, this may be a sign of a worm. Worms take up hard drive space when they replicate.
- Your email, SMS, or messaging service has suspicious activity: Many worms launch messaging campaigns in bulk to continue their path, infecting your contacts and other users. Worms will hijack your email account, SMS app, and online messaging services. If you get warnings and notifications, notice messages you didn’t send, or learn about contacts receiving strange messages from you, look into the issue immediately.
How to detect a computer worm on a Mac
If you have a computer worm on your Mac, then it’s essential that you remove it as quickly as possible. In general, macOS is a much tighter and more compartmentalized system compared to Windows, which makes it more difficult for malware to spread.
However, it’s not perfect, and criminals are always launching newer and better types of malware to get around Mac’s built-in security tools.
To correctly identify what type of malware you have, you need to run through a list of its behaviors. Here’s what to look out for when diagnosing a possible worm computer virus:
- Your computer slows to a crawl and/or crashes.
- Your network is suddenly extremely busy (worms may be trying to replicate or contact their home server).
- Your CPU shoots up to 100% when you’re barely using the computer.
- Your computer overheats due to the overworked CPU.
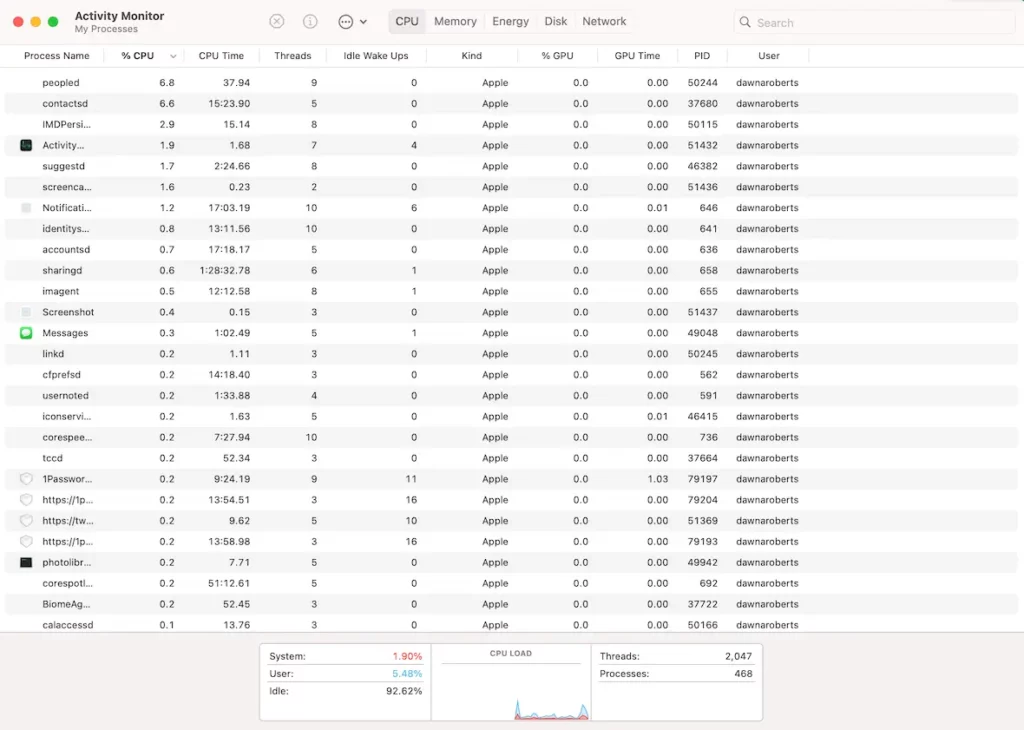
- Unknown and suspicious processes are running on Activity Monitor, sometimes with benign and credible names.
- Suspicious-looking files with weird file formats are on your computer, such as scripts.
- Unknown programs appear, running in the background. In many cases, Mac’s Gatekeeper and XProtect will stop this from happening, but some newer worms can get around and disable those programs.
In other words, if your computer starts behaving out of the ordinary, then there’s likely some form of malware hiding inside, and it’s time to take action.
How to remove a computer worm from your Mac
Now that you have identified the presence of a worm on your Mac, it’s time to get it off your device. Here are our recommendations for doing so. Don’t worry, we won’t be suggesting “have you tried turning it off then back on again?”
Before doing any of the following, disconnect your Mac from your network. That way, the worm can’t call home, and you’ve crippled it already.
Use Moonlock
To be sure that the worm is completely off your system, you should use a tool that will destroy the malware quickly and effectively. The best of these tools is Moonlock, a Mac protection and antivirus app.
You could try to remove the computer worm manually, but how do you know you removed it entirely? It’s better to use an antivirus app that knows what it’s doing and knows where to look.
After you sign up for the free trial and install Moonlock, its real-time protection will instantly find malware in the most vulnerable places of your Mac. To find dormant malware, select the Malware Scanner feature and run it. Delete everything it finds.
Check Activity Monitor
Some of the nasties that worms bring are scripts that will run malicious processes on your device. An essential step is to open your Activity Monitor and look for any suspicious running processes.
How do you identify these processes? Look for ones with garbage names and those taking up a disproportionate amount of CPU. Run a web search for the process names to make sure you’re not shutting down any legitimate system files.
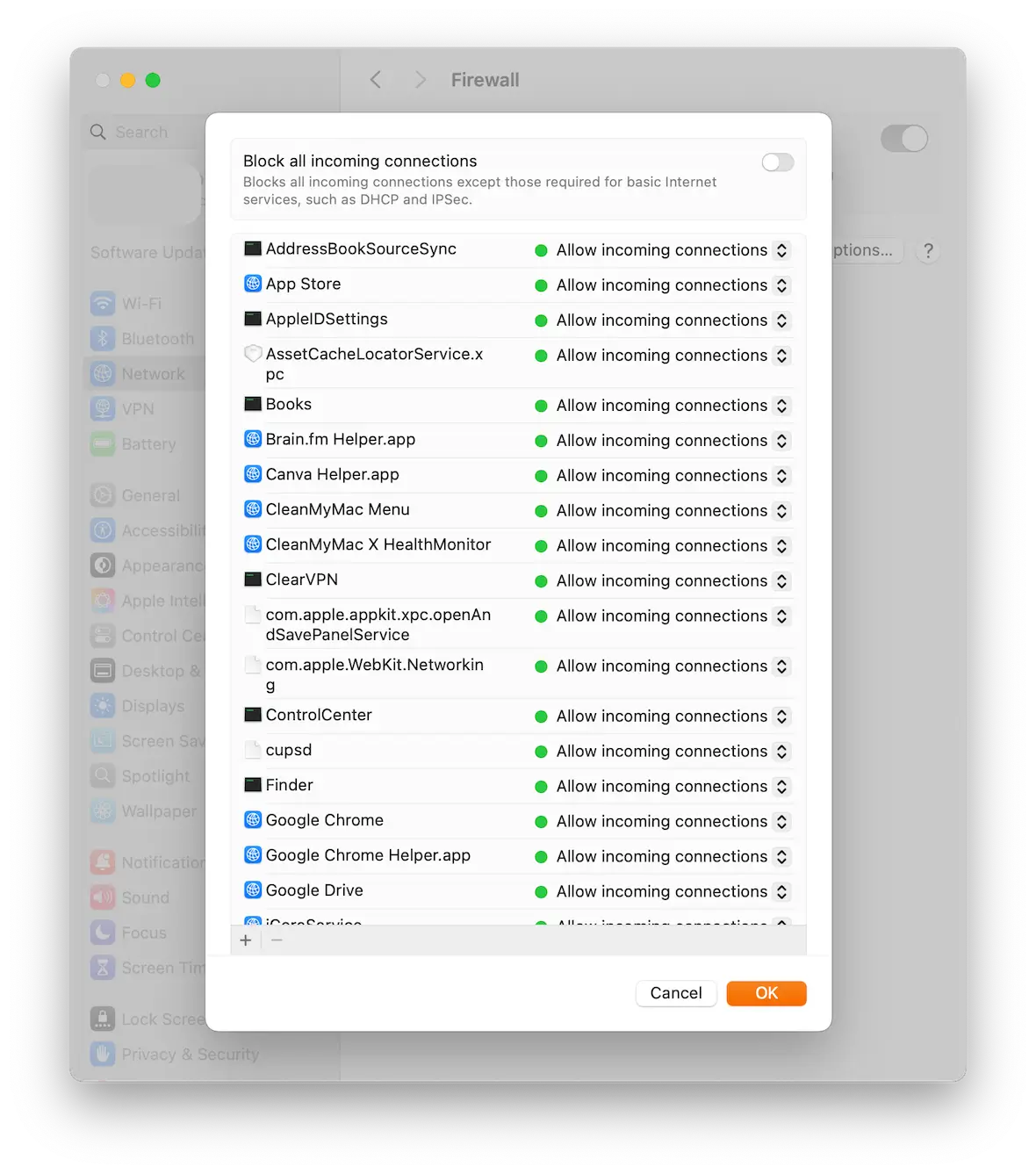
Check the firewall
One of the things a worm does is lower your system defenses to help it do its job. Thus, the next step is to check to see if your firewall has been disabled. Go to System Settings > Network > Firewall and enable it if it’s off.
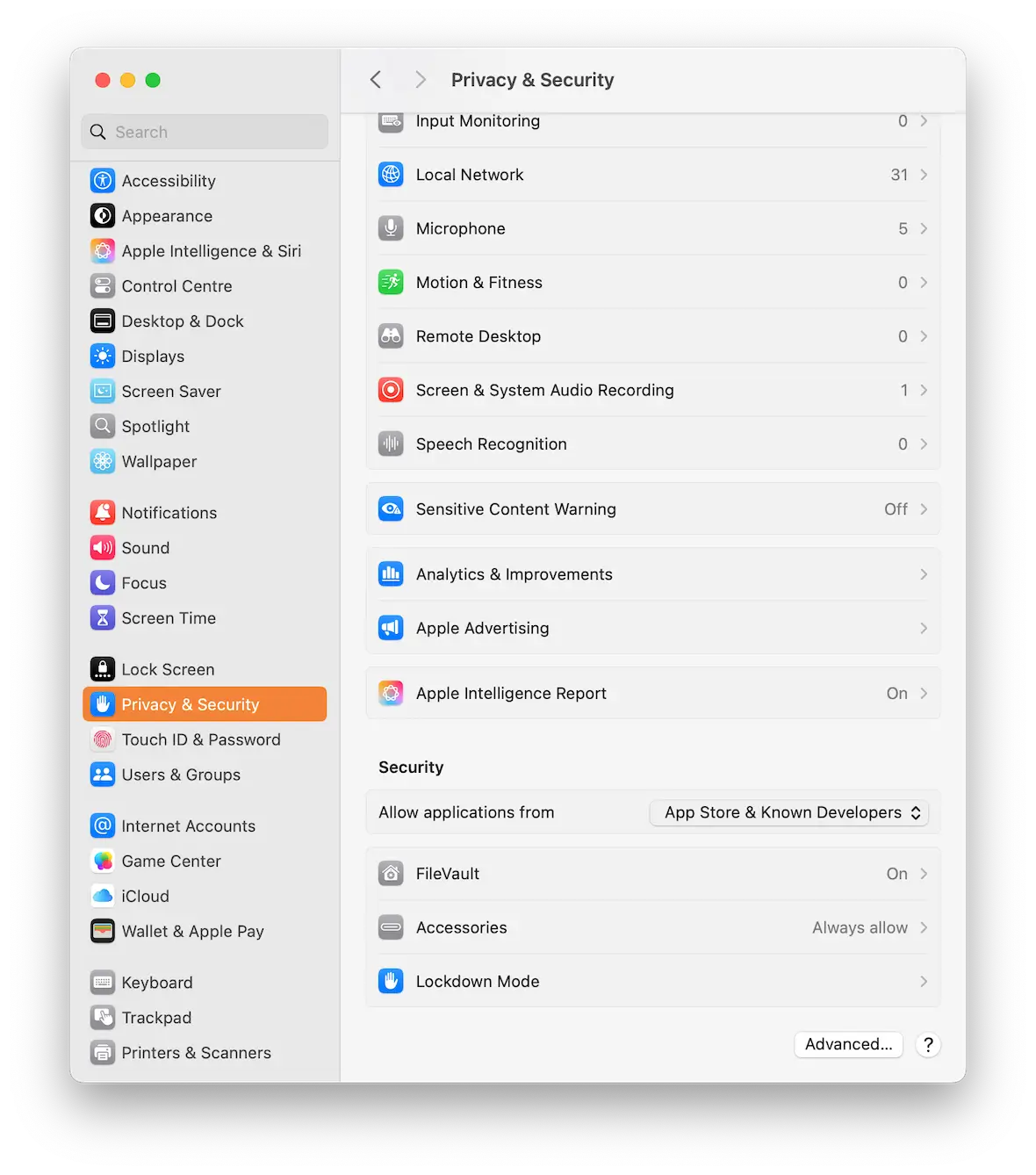
Remove unknown apps and processes
Next, go to Privacy & Security and check for unknown apps and processes. Then go to General > Device Management and remove any unknown configuration profiles.
Delete caches and temp files
Delete browser caches and temp files by going into your browser settings and wiping all browsing data.
Change the passwords for essential accounts and enable 2FA
In case the worm managed to get into an important online account, it would be prudent to change the passwords on those accounts and enable 2-factor authentication.
Wipe and reformat macOS
This is obviously the most extreme option, but it may be the only option if your files are damaged and you’re not 100% confident that the worm is gone. Luckily, Apple has streamlined the wiping and resetting process to make it easier and faster.
The difference between a computer worm and other malware
Worms are a unique kind of malware. They can do many things that other malicious software can’t do, such as self-replicate independently. They also have other impressive tricks under their sleeves, such as speed and the ability to search for other devices. Let’s look at the differences between worms and other types of malware.
Worm vs. Trojan
The main difference between a Trojan and a worm is how they infect a device. Trojans get their name from the hollow wooden horse used by the Ancient Greeks used to breach the walls of Troy by hiding soldiers inside during the Trojan War. A Trojan malware behaves in the same way. It appears to its victims as a piece of legitimate software but contains malware hidden within it. Worms do not use this technique.
Another difference is that Trojans usually require that users download and install a program. At the same time, worms never present themselves to users but instead breach devices undetected, requiring no action from the victim. Trojans do not have the self-replicating ability that worms have, but they can both open backdoors and spread through networks.
Worm vs. virus
Viruses, like Trojans, require human action to initiate. This means a virus can only begin causing damage when a user downloads and runs the program. While both viruses and worms can replicate, they do so differently.
Like a worm, a virus can spread from one computer to another, leaving infections behind as it travels, but every time it moves, it needs to trick the new user into installing it. Worms don’t need the victim to take any action.
What is the most famous computer worm?
The two worms that come to mind when thinking about the most infamous worms in cybersecurity history are WannaCry and Stuxnet.
The 2017 WannaCry ransomware cryptoworm infected 230,000 computers in 150 countries in just a couple of hours, sending shockwaves across businesses, politics, government, organizations, and the cyber security industry.
On the other hand, Stuxnet stands as the most sophisticated worm ever created. It was discovered in 2010, but experts believe it has operated since 2005. Stuxnet is more than a worm; it is a cyberweapon. It was developed under an operation run by the United States and Israel under the code name: Operation Olympic Games.
Stuxnet is believed to be responsible for causing damage to Iran’s nuclear program. The worm is not only digitally capable but can even control industrial machinery using infected hosts. Estimates say the worm infected more than 200,000 computers and caused damage or disruption to over 1,000 industrial operations.
Other notorious examples of computer worms
Many other computer worms have jumped to fame due to their attacks. Here are some of the most notorious:
The Morris worm or Internet worm: Released on November 2, 1988, this worm exploited weak passwords to infect thousands of computers in just 10 minutes. Estimates place the economic impact of the attack as high as $10 million.
The Bagle worm: Also known as the Beagle, Mitglieder, or Lodeight, was launched on January 18, 2004. The mass mailer worm malware initially infected 120,000 computers. The Bagle worm led to several variants. The Bagle botnet comprised an estimated 150,000-230,000 computers infected with the Bagle worm.
Conficker (AKA Downup, Downadup, or Kido): This worm exploited flaws in the Windows operating system and infected millions of computers in over a hundred countries.
SQL Slammer: The 2003 SQL Slammer, a brute-force worm, spread at lightning speed, infecting about 75,000 victims in just 10 minutes.
ILOVEYOU: This worm infected over ten million Windows personal computers when it launched in May 2000. It spread as an email message with a subject line that read “ILOVEYOU.” The worm preyed on a Windows vulnerability and used attached malware worm files.
What damage can a computer worm cause?
As we’ve already mentioned, worms are self-replicating, jumping from machine to machine and quickly overwhelming a network. Consequently, they are capable of an immense amount of damage, including the following issues.
Data loss and/or data corruption
When a worm gets onto a computer, it will immediately start looking for data to corrupt and steal. It can delete files, encrypt them, or corrupt them (making them inaccessible).
It can bring down the network
If a worm self-replicates and jumps from computer to computer in a network, pretty soon, it will overwhelm the network and cause it to crash. This will have a huge knock-on effect on businesses if their network goes down — even more so if the worm crashes the computers it affects.
Disruption of businesses and essential services
If a worm gets into a business’s computer network, it could result in huge financial losses and potential ruin. If computers running essential emergency services are brought down, this could lead to chaos and even potential loss of life.
Privacy breaches
Many attackers who use worms are searching for data to steal. This can be anything from credit card numbers to social security numbers and account login credentials.
How to prevent your Mac from getting infected with a worm
Worms sound unstoppable and extremely dangerous. But you can take simple steps to prevent computer worms from infecting your Mac.
Be aware of suspicious messages
While worms can breach your computer through networks, many attackers still use email, SMS, messaging, social media, malicious websites, and other social engineering techniques to trick you into clicking links or downloading files. Never open attachments from unknown contacts you don’t trust. Run antimalware on your communication channels, and be vigilant of strange messages.
Keep your firewalls up!
Firewalls are critical to keeping data secure. Fortunately, Macs have built-in firewalls that can be activated with just a few clicks. Combined with antimalware and firewalls, they are the most effective resources to stop worm attacks before they happen.
To enable your Mac’s firewall (macOS Ventura):
- Choose the Apple menu and select System Preferences.
- Now click Network and select Firewall. (For macOS Monterey and Big Sur, click Preferences, then Security & Privacy, then Firewall).
- Turn Firewall on.
- Click on Options for additional security settings (for example, allow only specified or essential apps and services, or turn on “Enable stealth mode”).

Update your operating system, software, and apps
Worms that use internet networks to spread exploit vulnerabilities found in operating systems, software, programs, and web and mobile applications. Apple developers are constantly fighting against cybercriminals.
That said, hackers will always find new ways to bypass existing Mac security features, and Apple cybersecurity experts will patch those vulnerabilities. Updates often include security patches, which are essential to stop the threats that are currently out there. Make sure you keep your Mac system fully updated.
The history of computer worms is fascinating, but its present and future states are concerning. Worms will continue evolving and are poised to become more dangerous every day. Understanding how a worm works, its symptoms, and what actions you can take to prevent them is critical. Stay informed and keep your guard up.